Epidemiological Survey of Human Alphaherpesvirus 2 (HSV-2) Infection in Indigenous People of Dourados Municipality, Central Brazil
- PMID: 37104324
- PMCID: PMC10143357
- DOI: 10.3390/tropicalmed8040197
Epidemiological Survey of Human Alphaherpesvirus 2 (HSV-2) Infection in Indigenous People of Dourados Municipality, Central Brazil
Abstract
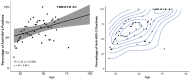
Sexually transmitted Human alphaherpesvirus 2 (HSV-2) causes genital ulcers, especially among sexually active adolescents and adults. We estimated the exact prevalence of anti-HSV-2 antibodies and correlated it with the demographic and behavioral aspects of the Indigenous population of the Jaguapirú and Bororó villages (Dourados, Mato Grosso do Sul (MS), Brazil). In total, 1360 individuals (>18 years old) were administered serologic tests. The prevalence of anti-HSV-2 IgM was 12.9%, that of anti-HSV-2 IgG was 57.2%, and 8.5% cases tested positive for both HSV-2 IgM and IgG. The prevalence of anti-HSV-2 antibodies was higher in females (59.5%) compared to males (49%), with an OR of 0.64 (0.49-0.83). Anti-HSV-2 antibodies were found in 14.2%, 12.3%, 15.4%, and 14.5% of participants with urinary problems, genital wounds, genital warts, and urethral discharge, respectively. In summary, the seroprevalence of HSV-2 in the Indigenous population was five times higher than that reported in the general adult Brazilian population. Educational level, income level, smoking, condom use, incarceration, illicit drug abuse, the sharing of used needles and syringes without adequate disinfection, homosexual relationships, prostitution, the sexual practices among drug users, and avoidance of contraceptive methods could contribute to the facilitation of HSV-2 transmission in the Indigenous population. Our results may help develop culturally appropriate intervention programs that eliminate health-access barriers and improve the implementation of public health policies aimed at promoting information regarding and preventing, treating, and controlling HSV-2 infection in Brazilian Indigenous populations.
Keywords: ethnicity; human alphaherpesvirus 2; human herpes virus 2; indigenous.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Brazilian Geographic and Statistics Institute IBGE. Indigenous in the 2010 Population Census. [(accessed on 26 October 2022)]; Available online: https://indigenas.ibge.gov.br/images/indigenas/estudos/indigena_censo201....
-
- Coelho R. ONTRIBUIÇÕES Para o Estudo da Demografia do Brasil. (Estudos de Estatística Teórica e Aplicada) 2nd ed. IBGE; Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: 1970. A Composição da População Segundo a Cor no Brasil e Nas Diversas Regiões Fisiográficas e Unidades da Federação, em 1950; pp. 68–197.
-
- SECID/MS Subsecretaria Especial de Cidadania. Governo do Estado de Mato Grosso do Sul. [(accessed on 26 October 2022)]; Available online: http://www.ms.gov.br/em-quatro-ano-governo-promove-acoes-e-executa-progr...
-
- de Alcantara M.L.B., Moure W., Trajber Z., Machado I.R. Equipe de Jovens da Ação dos Jovens Indígenas de Dourados-MS. A percepção do suicídio como inseparável das outras formas de violência segundo os/as jovens indígenas: Um estudo de caso da Reserva Indígena de Dourados. Rev. Med. 2020;99:305–318.
-
- Mota J.G.B., Cavalcante T.L.V. Reserva Indígena de Dourados: Histórias e Desafios Contemporâneos, 285. Ebook. Karywa; São Leopoldo, Brazil: 2019. 285p.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

