Sophorolipid Candidates Demonstrate Cytotoxic Efficacy against 2D and 3D Breast Cancer Models
- PMID: 37104545
- PMCID: PMC10760934
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00804
Sophorolipid Candidates Demonstrate Cytotoxic Efficacy against 2D and 3D Breast Cancer Models
Abstract
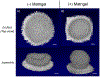
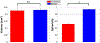
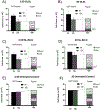
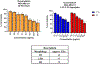
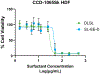
Sophorolipids are biosurfactants derived from the nonpathogenic yeasts such as Starmerella bombicola with potential efficacy in anticancer applications. Simple and cost-effective synthesis of these drugs makes them a promising alternative to traditional chemotherapeutics, pending their success in preliminary drug-screening. Drug-screening typically utilizes 2D cell monolayers due to their simplicity and ease of high-throughput assessment. However, 2D assays fail to capture the complexity and 3D context of the tumor microenvironment and have consequently been implicated in the high percentage of drugs investigated in vitro that later fail in clinical trials. Herein, we screened two sophorolipid candidates and a clinically-used chemotherapeutic, doxorubicin, on in vitro breast cancer models ranging from 2D monolayers to 3D spheroids, employing optical coherence tomography to confirm these morphologies. We calculated corresponding IC50 values for these drugs and found one of the sophorolipids to have comparable toxicities to the chemotherapeutic control. Our findings show increased drug resistance associated with model dimensionality, such that all drugs tested showed that 3D spheroids exhibited higher IC50 values than their 2D counterparts. These findings demonstrate promising preliminary data to support the use of sophorolipids as a more affordable alternative to traditional clinical interventions and demonstrate the importance of 3D tumor models in assessing drug response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Peng Y; Totsingan F; Meier MAR; Steinmann M; Wurm F; Koh A; Gross RA Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol 2015, 117 (2), 217–228.
-
- Singh SK; Felse AP; Nunez A; Foglia TA; Gross RA J. Org. Chem 2003, 68 (14), 5466–5477. - PubMed
-
- Bisht KS; Gross RA; Kaplan DL J. Org. Chem 1999, 64 (3), 780–789. - PubMed
-
- Shao L; Song X; Ma X; Li H; Qu YJ Surg. Res 2012, 173 (2), 286–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

