The contribution of historical processes to contemporary extinction risk in placental mammals
- PMID: 37104572
- PMCID: PMC10184782
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abn5856
The contribution of historical processes to contemporary extinction risk in placental mammals
Abstract
Species persistence can be influenced by the amount, type, and distribution of diversity across the genome, suggesting a potential relationship between historical demography and resilience. In this study, we surveyed genetic variation across single genomes of 240 mammals that compose the Zoonomia alignment to evaluate how historical effective population size (Ne) affects heterozygosity and deleterious genetic load and how these factors may contribute to extinction risk. We find that species with smaller historical Ne carry a proportionally larger burden of deleterious alleles owing to long-term accumulation and fixation of genetic load and have a higher risk of extinction. This suggests that historical demography can inform contemporary resilience. Models that included genomic data were predictive of species' conservation status, suggesting that, in the absence of adequate census or ecological data, genomic information may provide an initial risk assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests:
Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
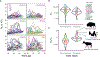
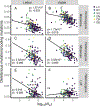

References
-
- Barnosky AD, Matzke N, Tomiya S, Wogan GOU, Swartz B, Quental TB, Marshall C, McGuire JL, Lindsey EL, Maguire KC, Mersey B, Ferrer EA, Has the Earth’s sixth mass extinction already arrived? Nature. 471, 51–57 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Ceballos G, Ehrlich AH, Ehrlich PR, The Annihilation of Nature: Human Extinction of Birds and Mammals (JHU Press, 2015).
-
- Hansson B, Morales HE, van Oosterhout C, Comment on “Individual heterozygosity predicts translocation success in threatened desert tortoises.” Science. 372 (2021), p. eabh1105. - PubMed
-
- Hansson B, Westerberg L, On the correlation between heterozygosity and fitness in natural populations. Molecular Ecology. 11 (2002), pp. 2467–2474. - PubMed

