T-Helper 22 Cell Type Responses to Nickel in Contact Allergic Subjects Are Associated with T-Helper 1, T-Helper 2, and T-Helper 17 Cell Cytokine Profile Responses and Patch Test Reactivity
- PMID: 37105142
- PMCID: PMC10413796
- DOI: 10.1159/000530105
T-Helper 22 Cell Type Responses to Nickel in Contact Allergic Subjects Are Associated with T-Helper 1, T-Helper 2, and T-Helper 17 Cell Cytokine Profile Responses and Patch Test Reactivity
Abstract
Introduction: Contact allergy to nickel (Ni) is a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction mediated by Ni-reactive T cells producing the hallmark cytokines of several T-helper cell (Th) populations including IFN-γ (Th1), IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 (Th2), and IL-17A (Th17). IL-22-expressing CD4+ cells, which could be either Th17 co-expressing IL-22 or Th22, expressing IL-22 in the absence of IL-17A, have also been found in Ni-provoked skin of allergic subjects. It has been unclear if Ni-reactive T cells consist of distinct Th cell type populations or if they secrete a mix of Th cell hallmark cytokines. The aim herein was to assess if cellular cytokine responses to Ni, in ex vivo-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from Ni-allergic subjects, include not only Th1, Th2, and Th17 but also Th22 hallmark cytokines and to define if the cytokines are produced by distinct cell populations representing different Th profiles.
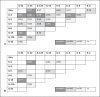
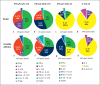
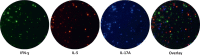
Methods: PBMC from Ni-allergic subjects (n = 15) with different degrees of patch test reactivity and non-allergic controls (n = 5) were in vitro stimulated with Ni. Cytokine levels in PBMC supernatants were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-3, IL-5, IL-6, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-22, and IL-31). FluoroSpot was used to assess if individual Ni-reactive cells produced single, or combinations of, cytokines representing different Th profiles. Cytokine combinations analyzed were IL-17A/IL-22/IFN-γ, IL-5/IL-17A/IFN-γ, IL-13/IL-22/IFN-γ, and IL-5/IL-13.
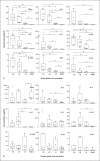
Results: IL-22 as well as all other cytokines measured by ELISA were induced by Ni at higher levels in PBMC from allergic versus non-allergic subjects, with higher levels being associated with stronger patch test reactivity. The levels of most Ni-induced cytokines were positively correlated with each other; IL-2 displayed the highest correlation with other cytokines and IL-6 the lowest. FluoroSpot analysis showed that Th signature cytokines, IFN-γ (Th1), IL-5 and IL-13 (Th2), IL-17A (Th17), and IL-22 (Th22), were almost exclusively produced by distinct cell populations.
Conclusion: Distinct Th cell populations, including Ni-reactive cells displaying Th1, Th2, Th17, and Th22 cytokine profiles, are all increased in PBMC from Ni-allergic subjects and positively associated with patch test reactivity. The relevance of these different Th profile populations for the up- or down-regulation of inflammatory reactions in the skin of Ni-allergic subjects remains to be clarified.
Keywords: Antigen specificity; Cytokines; Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; FluoroSpot; Nickel allergy; T-cell responses.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Khosro Masjedi and Niklas Ahlborg are employed by Mabtech AB, Sweden. Several of the reagents used in this study are manufactured by Mabtech. Mabtech had no influence on the content of this study or interpretation of results. Magnus Bruze has no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nickel elicits concomitant and correlated in vitro production of Th1-, Th2-type and regulatory cytokines in subjects with contact allergy to nickel.Scand J Immunol. 2005 Sep;62(3):289-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2005.01673.x. Scand J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16179016
-
Nickel-induced IL-10 down-regulates Th1- but not Th2-type cytokine responses to the contact allergen nickel.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Mar;143(3):494-502. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03018.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16487249 Free PMC article.
-
Nickel, cobalt, chromium, palladium and gold induce a mixed Th1- and Th2-type cytokine response in vitro in subjects with contact allergy to the respective metals.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Dec;146(3):417-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03226.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17100760 Free PMC article.
-
CD4 T Helper Cell Subsets and Related Human Immunological Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 28;21(21):8011. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218011. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33126494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of T Helper 1, T Helper 17 and Regulatory T Cells in the Pathogenesis of Sarcoidosis.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016 Aug;15(4):334-339. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27921415 Review.
Cited by
-
The Interaction Among Effector, Regulatory, and Tγδ Cells Determines the Development of Allergy or Tolerance to Chromium.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 19;14(4):1370. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041370. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kapsenberg ML, Wierenga EA, Stiekema FE, Tiggelman AM, Bos JD. Th1 lymphokine production profiles of nickel-specific CD4+T-lymphocyte clones from nickel contact allergic and non-allergic individuals. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Jan;98(1):59–63. - PubMed
-
- Jakobson E, Masjedi K, Ahlborg N, Lundeberg L, Karlberg AT, Scheynius A. Cytokine production in nickel-sensitized individuals analysed with enzyme-linked immunospot assay possible implication for diagnosis. Br J Dermatol. 2002 Sep;147(3):442–449. - PubMed
-
- Minang JT, Troye-Blomberg M, Lundeberg L, Ahlborg N. Nickel elicits concomitant and correlated in vitro production of Th1-Th2-type and regulatory cytokines in subjects with contact allergy to nickel. Scand J Immunol. 2005 Sep;62(3):289–296. - PubMed
-
- Dillon SR, Sprecher C, Hammond A, Bilsborough J, Rosenfeld-Franklin M, Presnell SR, et al. Interleukin 31, a cytokine produced by activated T cells, induces dermatitis in mice. Nat Immunol. 2004 Jul;5(7):752–760. - PubMed
-
- Neis MM, Peters B, Dreuw A, Wenzel J, Bieber T, Mauch C, et al. Enhanced expression levels of IL-31 correlate with IL-4 and IL-13 in atopic and allergic contact dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006 Oct;118(4):930–937. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

