The Ying and Yang of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signalling within the Bone
- PMID: 37108099
- PMCID: PMC10139073
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24086935
The Ying and Yang of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signalling within the Bone
Abstract
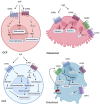
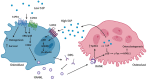
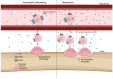
Bone remodelling is a highly active and dynamic process that involves the tight regulation of osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and their progenitors to allow for a balance of bone resorption and formation to be maintained. Ageing and inflammation are risk factors for the dysregulation of bone remodelling. Once the balance between bone formation and resorption is lost, bone mass becomes compromised, resulting in disorders such as osteoporosis and Paget's disease. Key molecules in the sphingosine-1-phosphate signalling pathway have been identified for their role in regulating bone remodelling, in addition to its more recognised role in inflammatory responses. This review discusses the accumulating evidence for the different, and, in certain circumstances, opposing, roles of S1P in bone homeostasis and disease, including osteoporosis, Paget's disease, and inflammatory bone loss. Specifically, we describe the current, often conflicting, evidence surrounding S1P function in osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and their precursors in health and disease, concluding that S1P may be an effective biomarker of bone disease and also an attractive therapeutic target for disease.
Keywords: S1P; bone; bone mineral density; osteoblast; osteoclast; osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Rutherford C., Childs S., Ohotski J., Mcglynn L., Riddick M., Macfarlane S., Tasker D., Pyne S., Pyne N.J., Edwards J., et al. Regulation of cell survival by sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor S1P1 via reciprocal ERK-dependent suppression of Bim and PI-3-kinase/protein kinase C-mediated upregulation of Mcl-1. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e927. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.455. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao Z., Chen Z., Zhao X., Pan F., Cai M., Wang T., Zhang H., Lu J.R., Lei M. Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes the differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes under the designated culturing conditions. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011;18:37. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-18-37. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

