Dual Blockade of TGF-β Receptor and Endothelin Receptor Synergistically Inhibits Angiotensin II-Induced Myofibroblast Differentiation: Role of AT1R/Gαq-Mediated TGF-β1 and ET-1 Signaling
- PMID: 37108136
- PMCID: PMC10138810
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24086972
Dual Blockade of TGF-β Receptor and Endothelin Receptor Synergistically Inhibits Angiotensin II-Induced Myofibroblast Differentiation: Role of AT1R/Gαq-Mediated TGF-β1 and ET-1 Signaling
Abstract
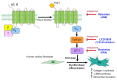
Angiotensin II (Ang II) upregulates transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) in various types of cells, and all of them act as profibrotic mediators. However, the signal transduction of angiotensin II receptor (ATR) for upregulation of TGF-β1 and ET-1, and their effectors that play an essential role in myofibroblast differentiation, are not fully understood. Therefore, we investigated the ATR networking with TGF-β1 and ET-1 and identified the signal transduction of these mediators by measuring the mRNA expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagen I using qRT-PCR. Myofibroblast phenotypes were monitored by α-SMA and stress fiber formation with fluorescence microscopy. Our findings suggested that Ang II induced collagen I and α-SMA synthesis and stress fiber formation through the AT1R/Gαq axis in adult human cardiac fibroblasts (HCFs). Following AT1R stimulation, Gαq protein, not Gβγ subunit, was required for upregulation of TGF-β1 and ET-1. Moreover, dual inhibition of TGF-β and ET-1 signaling completely inhibited Ang II-induced myofibroblast differentiation. The AT1R/Gαq cascade transduced signals to TGF-β1, which in turn upregulated ET-1 via the Smad- and ERK1/2-dependent pathways. ET-1 consecutively bound to and activated endothelin receptor type A (ETAR), leading to increases in collagen I and α-SMA synthesis and stress fiber formation. Remarkably, dual blockade of TGF-β receptor and ETR exhibited the restorative effects to reverse the myofibroblast phenotype induced by Ang II. Collectively, TGF-β1 and ET-1 are major effectors of AT1R/Gαq cascade, and therefore, negative regulation of TGF-β and ET-1 signaling represents a targeted therapeutic strategy for the prevention and restoration of cardiac fibrosis.
Keywords: TGF-β1; angiotensin II; angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB); cardiac fibrosis; endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA); endothelin-1; myofibroblast differentiation; α-SMA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gαq protein-biased ligand of angiotensin II type 1 receptor mediates myofibroblast differentiation through TGF-β1/ERK axis in human cardiac fibroblasts.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 15;951:175780. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175780. Epub 2023 May 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37209939
-
Endothelin-1 Induces Cell Proliferation and Myofibroblast Differentiation through the ETAR/Gαq/ERK Signaling Pathway in Human Cardiac Fibroblasts.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 24;24(5):4475. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054475. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901906 Free PMC article.
-
Macitentan inhibits the transforming growth factor-β profibrotic action, blocking the signaling mediated by the ETR/TβRI complex in systemic sclerosis dermal fibroblasts.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Sep 10;17(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0754-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26357964 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-beta1 and angiotensin networking in cardiac remodeling.Cardiovasc Res. 2004 Aug 15;63(3):423-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.04.030. Cardiovasc Res. 2004. PMID: 15276467 Review.
-
Angiotensin-TGF-beta 1 crosstalk in human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: autocrine mechanisms in myofibroblasts and macrophages.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(12):1247-56. doi: 10.2174/138161207780618885. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17504233 Review.
Cited by
-
IL24 Expression in Synovial Myofibroblasts: Implications for Female Osteoarthritis Pain through Propensity Score Matching Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Apr 29;60(5):741. doi: 10.3390/medicina60050741. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38792924 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Inflammation-Associated Epicardial Adipose Tissue for Atrial Fibrillation Patients.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 22;26(7):36598. doi: 10.31083/RCM36598. eCollection 2025 Jul. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40776948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Therapeutics for Heart Failure: Focusing on cGMP Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 16;24(16):12866. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612866. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiology, molecular mechanisms, and genetics of atrial fibrillation.Hum Cell. 2024 Nov 6;38(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01145-z. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 39505800 Review.
References
-
- Aoki T., Fukumoto Y., Sugimura K., Oikawa M., Satoh K., Nakano M., Nakayama M., Shimokawa H. Prognostic impact of myocardial interstitial fibrosis in non-ischemic heart failure-Comparison between preserved and reduced ejection fraction heart failure. Circ. J. 2011;75:2605–2613. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-11-0568. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kato S., Saito N., Kirigaya H., Gyotoku D., Iinuma N., Kusakawa Y., Iguchi K., Nakachi T., Fukui K., Futaki M., et al. Prognostic significance of quantitative assessment of focal myocardial fibrosis in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015;191:314–319. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.05.048. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

