RUNX2 and Cancer
- PMID: 37108164
- PMCID: PMC10139076
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087001
RUNX2 and Cancer
Abstract
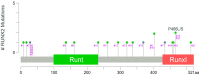
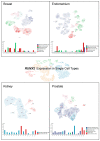
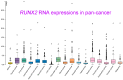
Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) is critical for the modulation of chondrocyte osteoblast differentiation and hypertrophy. Recently discovered RUNX2 somatic mutations, expressional signatures of RUNX2 in normal tissues and tumors, and the prognostic and clinical significance of RUNX2 in many types of cancer have attracted attention and led RUNX2 to be considered a biomarker for cancer. Many discoveries have illustrated the indirect and direct biological functions of RUNX2 in orchestrating cancer stemness, cancer metastasis, angiogenesis, proliferation, and chemoresistance to anticancer compounds, warranting further exploration of the associated mechanisms to support the development of a novel therapeutic strategy. In this review, we focus mainly on critical and recent research developments, including RUNX2's oncogenic activities, by summarizing and integrating the findings on somatic mutations of RUNX2, transcriptomic studies, clinical information, and discoveries about how the RUNX2-induced signaling pathway modulates malignant progression in cancer. We also comprehensively discuss RUNX2 RNA expression in a pancancer panel and in specific normal cell types at the single-cell level to indicate the potential cell types and sites for tumorigenesis. We expect this review to shed light on the recent mechanistical findings and modulatory role of RUNX2 in cancer progression and provide biological information that can guide new research in this field.
Keywords: RUNX2; cancer progression; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

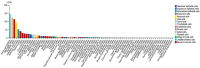
Similar articles
-
RUNX1 and cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022 May;1877(3):188715. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188715. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35271994 Review.
-
Updated Functional Roles of NAMPT in Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Niches.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 19;14(9):2059. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092059. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylase co-repressor complex control of Runx2 and bone formation.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2007;17(3):187-96. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v17.i3.20. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2007. PMID: 17725488 Review.
-
Expression of the ectodomain-releasing protease ADAM17 is directly regulated by the osteosarcoma and bone-related transcription factor RUNX2.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Nov;119(10):8204-8219. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26832. Epub 2018 Jun 19. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29923217 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Runx2 activity by estrogen receptor-alpha: implications for osteoporosis and breast cancer.Endocrinology. 2008 Dec;149(12):5984-95. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0680. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18755791 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exosome encapsulation of miR-205-5p suppresses neuroblastoma progression by targeting RUNX2.World J Pediatr Surg. 2025 Jun 24;8(3):e000993. doi: 10.1136/wjps-2024-000993. eCollection 2025. World J Pediatr Surg. 2025. PMID: 40575351 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC7 induction combined with standard-of-care chemotherapy provides a therapeutic advantage in t(4;11) infant B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Biomark Res. 2025 Jul 28;13(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s40364-025-00810-1. Biomark Res. 2025. PMID: 40722046 Free PMC article.
-
RUNX2 prompts triple negative breast cancer drug resistance through TGF-β pathway regulating breast cancer stem cells.Neoplasia. 2024 Feb;48:100967. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.100967. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Neoplasia. 2024. PMID: 38219710 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Regulation of the Human MGP Promoter: Identification of Downstream Repressors.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 23;25(23):12597. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312597. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684309 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling the ageing dependence of cancer evolutionary trajectories.Nat Rev Cancer. 2025 Jul 10. doi: 10.1038/s41568-025-00838-3. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40640377 Review.
References
-
- Bae S.C., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Inuzuka M., Kagoshima H., Shigesada K., Satake M., Ito Y. Isolation of PEBP2 alpha B cDNA representing the mouse homolog of human acute myeloid leukemia gene, AML1. Oncogene. 1993;8:809–814. - PubMed
-
- Komori T., Yagi H., Nomura S., Yamaguchi A., Sasaki K., Deguchi K., Shimizu Y., Bronson R.T., Gao Y.H., Inada M., et al. Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell. 1997;89:755–764. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80258-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

