Evaluation of Matrix Metalloproteases by Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Negative Biopsies as New Diagnostic Strategy in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 37108185
- PMCID: PMC10139111
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087022
Evaluation of Matrix Metalloproteases by Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Negative Biopsies as New Diagnostic Strategy in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
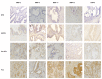
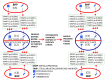
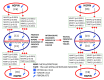
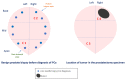
Usually, after an abnormal level of serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) or digital rectal exam, men undergo a prostate needle biopsy. However, the traditional sextant technique misses 15-46% of cancers. At present, there are problems regarding disease diagnosis/prognosis, especially in patients' classification, because the information to be handled is complex and challenging to process. Matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) have high expression by prostate cancer (PCa) compared with benign prostate tissues. To assess the possible contribution to the diagnosis of PCa, we evaluated the expression of several MMPs in prostate tissues before and after PCa diagnosis using machine learning, classifiers, and supervised algorithms. A retrospective study was conducted on 29 patients diagnosed with PCa with previous benign needle biopsies, 45 patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BHP), and 18 patients with high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN). An immunohistochemical study was performed on tissue samples from tumor and non-tumor areas using specific antibodies against MMP -2, 9, 11, and 13, and the tissue inhibitor of MMPs -3 (TIMP-3), and the protein expression by different cell types was analyzed to which several automatic learning techniques have been applied. Compared with BHP or HGPIN specimens, epithelial cells (ECs) and fibroblasts from benign prostate biopsies before the diagnosis of PCa showed a significantly higher expression of MMPs and TIMP-3. Machine learning techniques provide a differentiable classification between these patients, with greater than 95% accuracy, considering ECs, being slightly lower when considering fibroblasts. In addition, evolutionary changes were found in paired tissues from benign biopsy to prostatectomy specimens in the same patient. Thus, ECs from the tumor zone from prostatectomy showed higher expressions of MMPs and TIMP-3 compared to ECs of the corresponding zone from the benign biopsy. Similar differences were found for expressions of MMP-9 and TIMP-3, between fibroblasts from these zones. The classifiers have determined that patients with benign prostate biopsies before the diagnosis of PCa showed a high MMPs/TIMP-3 expression by ECs, so in the zone without future cancer development as in the zone with future tumor, compared with biopsy samples from patients with BPH or HGPIN. Expression of MMP -2, 9, 11, and 13, and TIMP-3 phenotypically define ECs associated with future tumor development. Also, the results suggest that MMPs/TIMPs expression in biopsy tissues may reflect evolutionary changes from prostate benign tissues to PCa. Thus, these findings in combination with other parameters might contribute to improving the suspicion of PCa diagnosis.
Keywords: automatic learning techniques; cancer diagnosis; cancer-associated fibroblast; matrix metalloproteinases; tumor stroma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of the expression of metalloproteases (MMP-2, MMP-9, MMP-11 and MMP-13) and the tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 3 (TIMP-3) between previous negative biopsies and radical prostatectomies.Actas Urol Esp (Engl Ed). 2020 Mar;44(2):78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.acuro.2019.10.004. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Actas Urol Esp (Engl Ed). 2020. PMID: 31899007 English, Spanish.
-
Differential expression of Low density lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein 1 (LRP-1) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in prostate gland: From normal to malignant lesions.Pathol Res Pract. 2017 Jan;213(1):66-71. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2016.11.008. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Pathol Res Pract. 2017. PMID: 27931798
-
Expression of ERG protein, a prostate cancer specific marker, in high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN): lack of utility to stratify cancer risks associated with HGPIN.BJU Int. 2012 Dec;110(11 Pt B):E751-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11557.x. Epub 2012 Oct 9. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 23046279
-
Prostate needle biopsies containing prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia or atypical foci suspicious for carcinoma: implications for patient care.J Urol. 2006 Mar;175(3 Pt 1):820-34. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)00337-X. J Urol. 2006. PMID: 16469560 Review.
-
In situ and intraductal epithelial proliferations of prostate: definitions and treatment implications. Part 1: Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia.BJU Int. 2012 Apr;109 Suppl 3:22-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11040.x. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 22458488 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic, diagnostic and prognostic values of TRIM proteins in prostate cancer.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Dec;75(6):1445-1453. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00534-9. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37921966 Review.
-
The Potential of Extracellular Matrix- and Integrin Adhesion Complex-Related Molecules for Prostate Cancer Biomarker Discovery.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 28;12(1):79. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010079. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38255186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumour microenvironment of urinary system.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Apr;15(4):e70299. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70299. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40195290 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kvale R., Moller B., Wahlqvist R., Fossa S.D., Berner A., Busch C., Kyrdalen A.E., Svindland A., Viset T., Halvorsen O.J. Concordance between Gleason scores of needle biopsies and radical prostatectomy specimens: A population-based study. BJU Int. 2009;103:1647–1654. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08255.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

