CIGB-258 Exerts Potent Anti-Inflammatory Activity against Carboxymethyllysine-Induced Acute Inflammation in Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish via the Protection of Apolipoprotein A-I
- PMID: 37108210
- PMCID: PMC10139093
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087044
CIGB-258 Exerts Potent Anti-Inflammatory Activity against Carboxymethyllysine-Induced Acute Inflammation in Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish via the Protection of Apolipoprotein A-I
Abstract
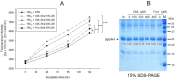
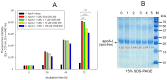
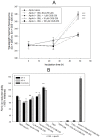
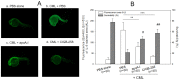
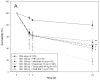
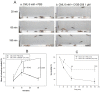
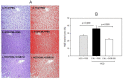
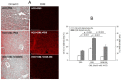
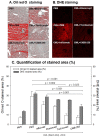
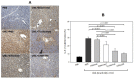
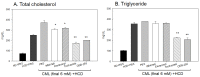
Inflammation and atherosclerosis are intimately associated via the production of dysfunctional high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and modification of apolipoprotein (apo) A-I. A putative interaction between CIGB-258 and apoA-I was investigated to provide mechanistic insight into the protection of HDL. The protective activity of CIGB-258 was tested in the CML-mediated glycation of apoA-I. The in vivo anti-inflammatory efficacy was compared in paralyzed hyperlipidemic zebrafish and its embryo in the presence of CML. Treatment of CML induced greater glycation extent of HDL/apoA-I and proteolytic degradation of apoA-I. In the presence of CML, however, co-treatment of CIGB-258 inhibited the glycation of apoA-I and protected the degradation of apoA-I, exerting enhanced ferric ion reduction ability. Microinjection of CML (500 ng) into zebrafish embryos resulted in acute death with the lowest survivability with severe developmental defects with interleukin (IL)-6 production. Conversely, a co-injection of CIGB-258 or Tocilizumab produced the highest survivability with a normal development speed and morphology. In hyperlipidemic zebrafish, intraperitoneal injection of CML (500 μg) caused the complete loss of swimming ability and severe acute death with only 13% survivability 3 h post-injection. A co-injection of the CIGB-258 resulted in a 2.2-fold faster recovery of swimming ability than CML alone, with higher survivability of approximately 57%. These results suggest that CIGB-258 protected hyperlipidemic zebrafish from the acute neurotoxicity of CML. Histological analysis showed that the CIGB-258 group had 37% lower infiltration of neutrophils in hepatic tissue and 70% lower fatty liver changes than those of the CML-alone group. The CIGB-258 group exhibited the smallest IL-6 expression in the liver and the lowest blood triglyceride level. CIGB-258 displayed potent anti-inflammatory activity in hyperlipidemic zebrafish by inhibiting apoA-I glycation, promoting rapid recovery from the paralysis of CML toxicity and suppression of IL-6, and lowering fatty liver changes.
Keywords: CIGB-258 (Jusvinza®); apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I); carboxymethyllysine (CML); high cholesterol diet; hyperinflammation; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of CIGB-258 against Acute Toxicity of Carboxymethyllysine in Paralyzed Zebrafish via Enhancement of High-Density Lipoproteins Stability and Functionality.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 4;23(17):10130. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710130. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077532 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Lipid-Free Apolipoprotein (apo) A-I and CIGB-258 in Acute-Phase Zebrafish via Stabilization of the apoA-I Structure to Enhance Anti-Glycation and Antioxidant Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 20;25(10):5560. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105560. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791598 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Wound Healing and Anti-Inflammatory Effects by Combination of CIGB-258 and Apolipoprotein A-I against Carboxymethyllysine Toxicity in Zebrafish: Insights into Structural Stabilization and Antioxidant Properties.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 28;13(9):1049. doi: 10.3390/antiox13091049. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334708 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory mechanism of Apolipoprotein A-I.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 8;15:1417270. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1417270. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39040119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro- or anti-inflammatory role of apolipoprotein A-1 in high-density lipoproteins?Swiss Med Wkly. 2013 May 25;143:w13781. doi: 10.4414/smw.2013.13781. eCollection 2013. Swiss Med Wkly. 2013. PMID: 23740387 Review.
Cited by
-
Prolonged Supplementation of Ozonated Sunflower Oil Bestows an Antiaging Effect, Improves Blood Lipid Profile and Spinal Deformities, and Protects Vital Organs of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) against Age-Related Degeneration: Two-Years Consumption Study.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 19;13(1):123. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010123. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275648 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Supplementation of Royal Jelly (Raydel®) Improves Zebrafish Growth, Embryo Production and Survivability, Blood Lipid Profile and Functionality of Vital Organs: A 72-Weeks' Consumption Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 1;17(3):324. doi: 10.3390/ph17030324. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543109 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Apolipoprotein A-I and CIGB-258 in Reconstituted High-Density Lipoproteins (rHDL) against Acute Toxicity of Carboxymethyllysine in Zebrafish and Its Embryo.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 28;17(2):165. doi: 10.3390/ph17020165. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399381 Free PMC article.
-
Ozonated Sunflower Oil Exerted Potent Anti-Inflammatory Activities with Enhanced Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration Abilities against Acute Toxicity of Carboxymethyllysine in Zebrafish with Improved Blood Lipid Profile.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 17;12(8):1625. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081625. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627620 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Profile Regulated by the Immunomodulatory Jusvinza Drug in Neutrophils Isolated from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Biomedicines. 2024 Nov 29;12(12):2740. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122740. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mak T.W., Saunders M.E. The Immune Response: Basic and Clinical Principles. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2005.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

