Improved Simulated-Daylight Photodynamic Therapy and Possible Mechanism of Ag-Modified TiO2 on Melanoma
- PMID: 37108223
- PMCID: PMC10138875
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087061
Improved Simulated-Daylight Photodynamic Therapy and Possible Mechanism of Ag-Modified TiO2 on Melanoma
Abstract
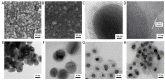
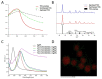
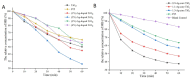
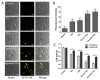
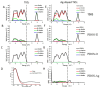
Simulated-daylight photodynamic therapy (SD-PDT) may be an efficacious strategy for treating melanoma because it can overcome the severe stinging pain, erythema, and edema experienced during conventional PDT. However, the poor daylight response of existing common photosensitizers leads to unsatisfactory anti-tumor therapeutic effects and limits the development of daylight PDT. Hence, in this study, we utilized Ag nanoparticles to adjust the daylight response of TiO2, acquire efficient photochemical activity, and then enhance the anti-tumor therapeutic effect of SD-PDT on melanoma. The synthesized Ag-doped TiO2 showed an optimal enhanced effect compared to Ag-core TiO2. Doping Ag into TiO2 produced a new shallow acceptor impurity level in the energy band structure, which expanded optical absorption in the range of 400-800 nm, and finally improved the photodamage effect of TiO2 under SD irradiation. Plasmonic near-field distributions were enhanced due to the high refractive index of TiO2 at the Ag-TiO2 interface, and then the amount of light captured by TiO2 was increased to induce the enhanced SD-PDT effect of Ag-core TiO2. Hence, Ag could effectively improve the photochemical activity and SD-PDT effect of TiO2 through the change in the energy band structure. Generally, Ag-doped TiO2 is a promising photosensitizer agent for treating melanoma via SD-PDT.
Keywords: Ag-core TiO2; Ag-doped TiO2; melanoma; simulated-daylight photodynamic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
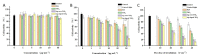


Similar articles
-
PEGylated silver doped zinc oxide nanoparticles as novel photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy against Leishmania.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Dec;77:230-8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.09.005. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 25266330
-
Carbon-Doped TiO2 Activated by X-Ray Irradiation for the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species to Enhance Photodynamic Therapy in Tumor Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 26;20(9):2072. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092072. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31035468 Free PMC article.
-
Solution-combustion synthesis of doped TiO2 compounds and its potential antileishmanial activity mediated by photodynamic therapy.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018 Jun;183:64-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.017. Epub 2018 Apr 13. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018. PMID: 29689488
-
Innovative strategies for enhanced tumor photodynamic therapy.J Mater Chem B. 2021 Sep 22;9(36):7347-7370. doi: 10.1039/d1tb01466h. J Mater Chem B. 2021. PMID: 34382629 Review.
-
Daylight photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis: an international consensus: International Society for Photodynamic Therapy in Dermatology.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012 Jun;26(6):673-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04386.x. Epub 2011 Dec 23. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012. PMID: 22211665 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress in Melanoma: Beneficial Antioxidant and Pro-Oxidant Therapeutic Strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 2;15(11):3038. doi: 10.3390/cancers15113038. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37297001 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

