Plasma Exosomal Non-Coding RNA Profile Associated with Renal Damage Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets in Lupus Nephritis
- PMID: 37108249
- PMCID: PMC10139178
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087088
Plasma Exosomal Non-Coding RNA Profile Associated with Renal Damage Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets in Lupus Nephritis
Abstract
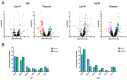
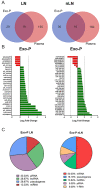
Despite considerable progress in our understanding of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathophysiology, patient diagnosis is often deficient and late, and this has an impact on disease progression. The aim of this study was to analyze non-coding RNA (ncRNA) packaged into exosomes by next-generation sequencing to assess the molecular profile associated with renal damage, one of the most serious complications of SLE, to identify new potential targets to improve disease diagnosis and management using Gene Ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis. The plasma exosomes had a specific ncRNA profile associated with lupus nephritis (LN). The three ncRNA types with the highest number of differentially expressed transcripts were microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). We identified an exosomal 29-ncRNA molecular signature, of which 15 were associated only with LN presence; piRNAs were the most representative, followed by lncRNAs and miRNAs. The transcriptional regulatory network showed a significant role for four lncRNAs (LINC01015, LINC01986, AC087257.1 and AC022596.1) and two miRNAs (miR-16-5p and miR-101-3p) in network organization, targeting critical pathways implicated in inflammation, fibrosis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and actin cytoskeleton. From these, a handful of potential targets, such as transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily binding proteins (activin-A, TGFB receptors, etc.), WNT/β-catenin and fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) have been identified for use as therapeutic targets of renal damage in SLE.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; bioinformatics enrichment analysis; exosomes; non-coding RNA; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of lupus nephritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 29;14:1326836. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1326836. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38223506 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of serum exosomal miRNA biomarkers in patients with lupus nephritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jun;44(6):2299-2310. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07447-3. Epub 2025 May 3. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40319190
-
Identification and analysis of the predictive urinary exosomal miR-195-5p in lupus nephritis based on renal miRNA-mRNA co-expression network.Lupus. 2022 Dec;31(14):1786-1799. doi: 10.1177/09612033221133684. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Lupus. 2022. PMID: 36223498
-
The role of non-coding RNA in lupus nephritis.Hum Cell. 2023 May;36(3):923-936. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00883-w. Epub 2023 Feb 25. Hum Cell. 2023. PMID: 36840837 Review.
-
Advances in the study of exosome-derived miRNAs in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.Lupus. 2023 Nov;32(13):1475-1485. doi: 10.1177/09612033231212280. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Lupus. 2023. PMID: 37906972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding the role of exosomal lncRNAs in rheumatic diseases: a review.PeerJ. 2023 Dec 13;11:e16434. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16434. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38107573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PiRNA Obtained through Liquid Biopsy as a Possible Cancer Biomarker.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 May 29;13(11):1895. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13111895. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37296747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small extracellular vesicle cargo as biomarkers in autoimmune rheumatic diseases: a systematic review.Rheumatol Int. 2025 Sep 1;45(9):211. doi: 10.1007/s00296-025-05953-w. Rheumatol Int. 2025. PMID: 40888924 Free PMC article.
-
The role of lncRNAs in AKI and CKD: Molecular mechanisms, biomarkers, and potential therapeutic targets.Genes Dis. 2024 Dec 30;12(3):101509. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101509. eCollection 2025 May. Genes Dis. 2024. PMID: 40083322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enrichment of RedoxifibromiR miR-21-5p in Plasma Exosomes of Hypertensive Patients with Renal Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 12;26(2):590. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020590. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perez-Hernandez J., Martinez-Arroyo O., Ortega A., Galera M., Solis-Salguero M.A., Chaves F.J., Redon J., Forner M.J., Cortes R. Urinary exosomal miR-146a as a marker of albuminuria, activity changes and disease flares in lupus nephritis. J. Nephrol. 2021;34:1157–1167. doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00832-y. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

