Assessing the Role of MicroRNAs in Predicting Breast Cancer Recurrence-A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37108278
- PMCID: PMC10138898
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087115
Assessing the Role of MicroRNAs in Predicting Breast Cancer Recurrence-A Systematic Review
Abstract
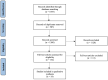
Identifying patients likely to develop breast cancer recurrence remains a challenge. Thus, the discovery of biomarkers capable of diagnosing recurrence is of the utmost importance. MiRNAs are small, non-coding RNA molecules which are known to regulate genetic expression and have previously demonstrated relevance as biomarkers in malignancy. To perform a systematic review evaluating the role of miRNAs in predicting breast cancer recurrence. A formal systematic search of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane databases was performed. This search was performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) checklist. A total of 19 studies involving 2287 patients were included. These studies identified 44 miRNAs which predicted breast cancer recurrence. Results from nine studies assessed miRNAs in tumour tissues (47.4%), eight studies included circulating miRNAs (42.1%), and two studies assessed both tumour and circulating miRNAs (10.5%). Increased expression of 25 miRNAs were identified in patients who developed recurrence, and decreased expression of 14 miRNAs. Interestingly, five miRNAs (miR-17-5p, miR-93-5p, miR-130a-3p, miR-155, and miR-375) had discordant expression levels, with previous studies indicating both increased and reduced expression levels of these biomarkers predicting recurrence. MiRNA expression patterns have the ability to predict breast cancer recurrence. These findings may be used in future translational research studies to identify patients with breast cancer recurrence to improve oncological and survival outcomes for our prospective patients.
Keywords: breast cancer; microRNAs; oncological outcomes; recurrence; survival outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Panels of circulating microRNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Nov;196(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06728-8. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 36085533
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of miRNAs for the detection of cervical cancer.Epigenomics. 2023 May;15(10):593-613. doi: 10.2217/epi-2023-0183. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Epigenomics. 2023. PMID: 37535320
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
MicroRNAs as biomarkers in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A systematic review of recent clinical evidence.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022 Feb;213:107130. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2022.107130. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 35066247
-
miRNAs as therapeutic predictors and prognostic biomarkers of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Aug;194(3):483-505. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06642-z. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35727379
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs as Molecular Biomarkers for the Characterization of Basal-like Breast Tumor Subtype.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 9;11(11):3007. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11113007. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38002007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Implications of MicroRNAs as Regulators and Biomarkers of Therapeutic Toxicities in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 11;24(16):12694. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612694. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: Emerging as Highly Promising Biomarkers for Early Breast Cancer Screening.J Clin Lab Med. 2023;6(3):273. Epub 2023 Sep 6. J Clin Lab Med. 2023. PMID: 37937319 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Molecular Morbidity Score-Can MicroRNAs Assess the Burden of Disease?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 24;25(15):8042. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158042. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of miRNAs as biomarkers in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 May 15;14:1374821. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1374821. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38812786 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davey M.G., Ryan É.J., McAnena P.F., Boland M.R., Barry M.K., Sweeney K.J., Malone C.M., McLaughlin R.J., Lowery A.J., Kerin M.J. Disease recurrence and oncological outcome of patients treated surgically with curative intent for estrogen receptor positive, lymph node negative breast cancer. Surg. Oncol. 2021;37:101531. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2021.101531. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical