SM22α Deletion Contributes to Neurocognitive Impairment in Mice through Modulating Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypes
- PMID: 37108281
- PMCID: PMC10138350
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087117
SM22α Deletion Contributes to Neurocognitive Impairment in Mice through Modulating Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypes
Abstract
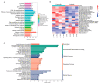
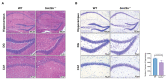
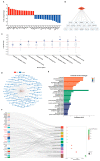
Considerable evidence now indicates that cognitive impairment is primarily a vascular disorder. The depletion of smooth muscle 22 alpha (SM22α) contributes to vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) switching from contractile to synthetic and proinflammatory phenotypes in the context of inflammation. However, the role of VSMCs in the pathogenesis of cognitive impairment remains undetermined. Herein, we showed a possible link between VSMC phenotypic switching and neurodegenerative diseases via the integration of multi-omics data. SM22α knockout (Sm22α-/-) mice exhibited obvious cognitive impairment and cerebral pathological changes, which were visibly ameliorated by the administration of AAV-SM22α. Finally, we confirmed that SM22α disruption promotes the expression of SRY-related HMG-box gene 10 (Sox10) in VSMCs, thereby aggravating the systemic vascular inflammatory response and ultimately leading to cognitive impairment in the brain. Therefore, this study supports the idea of VSMCs and SM22α as promising therapeutic targets in cognitive impairment to improve memory and cognitive decline.
Keywords: SRY-related HMG-box gene 10; cognitive impairment; inflammation; smooth muscle 22-alpha; vascular smooth muscle cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SM22α inhibits lamellipodium formation and migration via Ras-Arp2/3 signaling in synthetic VSMCs.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;311(5):C758-C767. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00033.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27629412
-
CKII-SIRT1-SM22α loop evokes a self-limited inflammatory response in vascular smooth muscle cells.Cardiovasc Res. 2017 Aug 1;113(10):1198-1207. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx048. Cardiovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28419207
-
C/EBP-Homologous Protein (CHOP) in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Regulates Their Proliferation in Aortic Explants and Atherosclerotic Lesions.Circ Res. 2015 May 22;116(11):1736-43. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.305602. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 25872946 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of SM22α in cellular plasticity and vascular diseases.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2012 Dec;12(2):119-25. doi: 10.2174/1871529x11202020119. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 23030444 Review.
-
Smooth muscle cell-driven vascular diseases and molecular mechanisms of VSMC plasticity.Cell Signal. 2018 Dec;52:48-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.08.019. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 30172025 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase ameliorates cerebral blood flow autoregulation and cognition in alzheimer's disease and diabetes-related dementia rat models.Geroscience. 2025 Jun;47(3):4429-4449. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01550-8. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39903369 Free PMC article.
-
The AICD interactome: implications in neurodevelopment and neurodegeneration.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Dec 19;52(6):2539-2556. doi: 10.1042/BST20241510. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 39670668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Ameliorates Cerebral Blood Flow Autoregulation and Cognition in Alzheimer's Disease and Diabetes-Related Dementia Rat Models.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 31:2024.08.30.610540. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.30.610540. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Geroscience. 2025 Jun;47(3):4429-4449. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01550-8. PMID: 39257786 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 91739301/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 91849102/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- H2019206028/Key Natural Science Foundation Projects of Hebei Province
- 20567635H/Key Natural Science Foundation Projects of Hebei Province
- H2021206006/Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

