Reduction in CgA-Derived CST Protein Level in HTR-8/SVneo and BeWo Trophoblastic Cell Lines Caused by the Preeclamptic Environment
- PMID: 37108287
- PMCID: PMC10138478
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087124
Reduction in CgA-Derived CST Protein Level in HTR-8/SVneo and BeWo Trophoblastic Cell Lines Caused by the Preeclamptic Environment
Abstract
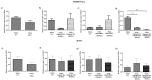
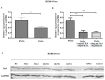
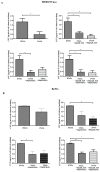
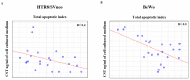
One of the most dangerous complications of pregnancy is preeclampsia (PE), a disease associated with a high risk of maternal and fetal mortality and morbidity. Although its etiology remains unknown, the placenta is believed to be at the center of ongoing changes. One of the hormones produced by the placenta is chromogranin A (CgA). Thus far, its role in pregnancy and pregnancy-related disorders is enigmatic, yet it is known that both CgA and its derived peptide catestatin (CST) are involved in the majority of the processes that are disturbed in PE, such as blood pressure regulation or apoptosis. Therefore, in this study, the influence of the preeclamptic environment on the production of CgA using two cell lines, HTR-8/SVneo and BeWo, was investigated. Furthermore, the capacity of trophoblastic cells to secrete CST to the environment was tested, as well as the correlation between CST and apoptosis. This study provided the first evidence that CgA and CST proteins are produced by trophoblastic cell lines and that the PE environment has an impact on CST protein production. Furthermore, a strong negative correlation between CST protein level and apoptosis induction was found. Hence, both CgA and its derived peptide CST may play roles in the complex process of PE pathogenesis.
Keywords: catestatin; chromogranin A; hypertension; preeclampsia; pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Role of Catestatin in Preeclampsia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 20;25(5):2461. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052461. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YAP Is Decreased in Preeclampsia and Regulates Invasion and Apoptosis of HTR-8/SVneo.Reprod Sci. 2018 Sep;25(9):1382-1393. doi: 10.1177/1933719117746784. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Reprod Sci. 2018. PMID: 29303055
-
MicroRNA-141 is upregulated in preeclamptic placentae and regulates trophoblast invasion and intercellular communication.Transl Res. 2016 Jun;172:61-72. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2016.02.012. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27012474
-
Chromogranin A demonstrates higher expression in preeclamptic placentas than in normal pregnancy.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021 Oct 7;21(1):680. doi: 10.1186/s12884-021-04139-z. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021. PMID: 34620125 Free PMC article.
-
Putative regulation of macrophage-mediated inflammation by catestatin.Trends Immunol. 2022 Jan;43(1):41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.11.002. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Trends Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34844850 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Catestatin in Preeclampsia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 20;25(5):2461. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052461. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catestatin in Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 7;26(6):2417. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062417. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Ideas for the Prevention and Treatment of Preeclampsia and Their Molecular Inspirations.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 28;24(15):12100. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512100. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Proteomics-Based Identification of the Biological Networks Mediating the Impact of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Trophoblast Cell Migration and Invasion, with Potential Implications for Maternal and Fetal Health.Proteomes. 2023 Oct 12;11(4):31. doi: 10.3390/proteomes11040031. Proteomes. 2023. PMID: 37873873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown M.A., Magee L.A., Kenny L.C., Karumanchi S.A., McCarthy F.P., Saito S., Hall D.R., Warren C.E., Adoyi G., Ishaku S. The hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: ISSHP classification, diagnosis & management recommendations for international practice. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018;13:291–310. - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee I., Dhar R., Singh S., Sharma J.B., Nag T.C., Mridha A.R., Jaiswal P., Biswas S., Karmakar S. Oxidative stress-induced impairment of trophoblast function causes preeclampsia through the unfolded protein response pathway. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:18415. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97799-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

