The Blinin Accumulation Promoted by CbMYB32 Involved in Conyza blinii Resistance to Nocturnal Low Temperature
- PMID: 37108302
- PMCID: PMC10139108
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087143
The Blinin Accumulation Promoted by CbMYB32 Involved in Conyza blinii Resistance to Nocturnal Low Temperature
Abstract
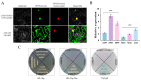
Blinin, a unique terpenoid from Conyza blinii (C. blinii), benefits our health even though this is not its primary function. Physiological and ecological studies have found that the great secondary metabolites participate in important biological processes and relate to species evolution, environmental adaptation, and so on. Moreover, our previous studies have shown that the metabolism and accumulation of blinin has a close correspondence with nocturnal low temperature (NLT). To find out the transcriptional regulation linker in the crosstalk between blinin and NLT, RNA-seq, comparative analysis, and co-expression network were performed. The results indicated that CbMYB32 is located in a nucleus without independent transcriptional activation activity and is probably involved in the metabolism of blinin. Furthermore, we compared the silence and overexpression of CbMYB32 with wild C. blinii. Compared with the overexpression and the wildtype, the CbMYB32 silence line lost more than half of the blinin and detected more peroxide under NLT. Finally, as a characteristic secret of C. blinii, it is reasonable to infer that blinin participates in the NLT adaptation mechanism and has contributed to the systematic evolution of C. blinii.
Keywords: Conyza blinii; nocturnal low temperature resistance; transcriptional regulation; unique terpenoid blinin; virus-induced gene silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

