β-Cyclodextrin Polymer-Based Fluorescence Enhancement Strategy via Host-Guest Interaction for Sensitive Assay of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 37108336
- PMCID: PMC10139410
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087174
β-Cyclodextrin Polymer-Based Fluorescence Enhancement Strategy via Host-Guest Interaction for Sensitive Assay of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
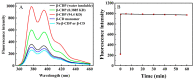
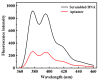
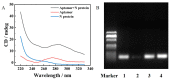
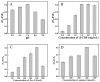
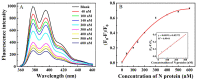
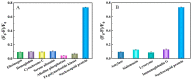
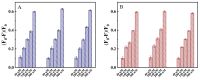
Nucleocapsid protein (N protein) is an appropriate target for early determination of viral antigen-based severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). We have found that β-cyclodextrin polymer (β-CDP) has shown a significant fluorescence enhancement effect for fluorophore pyrene via host-guest interaction. Herein, we developed a sensitive and selective N protein-sensing method that combined the host-guest interaction fluorescence enhancement strategy with high recognition of aptamer. The DNA aptamer of N protein modified with pyrene at its 3' terminal was designed as the sensing probe. The added exonuclease I (Exo I) could digest the probe, and the obtained free pyrene as a guest could easily enter into the hydrophobic cavity of host β-CDP, thus inducing outstanding luminescent enhancement. While in the presence of N protein, the probe could combine with it to form a complex owing to the high affinity between the aptamer and the target, which prevented the digestion of Exo I. The steric hindrance of the complex prevented pyrene from entering the cavity of β-CDP, resulting in a tiny fluorescence change. N protein has been selectively analyzed with a low detection limit (11.27 nM) through the detection of the fluorescence intensity. Moreover, the sensing of spiked N protein from human serum and throat swabs samples of three volunteers has been achieved. These results indicated that our proposed method has broad application prospects for early diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019.
Keywords: DNA aptamer; SARS-CoV-2; fluorescence enhancement; host–guest interaction; β-cyclodextrin polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amplified fluorescence detection of DNA based on catalyzed dynamic assembly and host-guest interaction between β-cyclodextrin polymer and pyrene.Talanta. 2015 Nov 1;144:529-34. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.06.087. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Talanta. 2015. PMID: 26452858
-
β-Cyclodextrin Polymer-Based Host-Guest Interaction and Fluorescence Enhancement of Pyrene for Sensitive Isocarbophos Detection.ACS Omega. 2022 Apr 8;7(15):12747-12752. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c07295. eCollection 2022 Apr 19. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35474801 Free PMC article.
-
Amplified fluorescence detection of adenosine via catalyzed hairpin assembly and host-guest interactions between β-cyclodextrin polymer and pyrene.Analyst. 2016 Apr 21;141(8):2502-7. doi: 10.1039/c5an02658j. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Analyst. 2016. PMID: 26999785
-
Steric hindrance regulated supramolecular assembly between β-cyclodextrin polymer and pyrene for alkaline phosphatase fluorescent sensing.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2016 Mar 5;156:131-7. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2015.12.001. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2016. PMID: 26679620
-
The utility of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in laboratory diagnosis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jul;36(7):e24534. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24534. Epub 2022 Jun 3. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35657146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hellewell J., Abbott S., Gimma A., Bosse N.I., Jarvis C.I., Russell T.W., Munday J.D., Kucharski A.J., Edmunds W.J., Funk S., et al. Feasibility of controlling COVID-19 outbreaks by isolation of cases and contacts. Lancet Glob. Health. 2020;8:e488–e496. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30074-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

