Modulation of Disease-Associated Pathways in Hidradenitis Suppurativa by the Janus Kinase 1 Inhibitor Povorcitinib: Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses of Two Phase 2 Studies
- PMID: 37108348
- PMCID: PMC10139090
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087185
Modulation of Disease-Associated Pathways in Hidradenitis Suppurativa by the Janus Kinase 1 Inhibitor Povorcitinib: Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses of Two Phase 2 Studies
Abstract
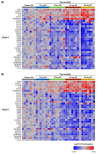
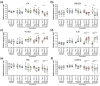
Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling (STAT) has been implicated in the pathophysiology of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). This study evaluated treatment-related transcriptomic and proteomic changes in patients with moderate-to-severe HS treated with the investigational oral JAK1-selective inhibitor povorcitinib (INCB054707) in two phase 2 trials. Lesional skin punch biopsies (baseline and Week 8) were taken from active HS lesions of patients receiving povorcitinib (15 or 30 mg) once daily (QD) or a placebo. RNA-seq and gene set enrichment analyses were used to evaluate the effects of povorcitinib on differential gene expression among previously reported gene signatures from HS and wounded skin. The number of differentially expressed genes was the greatest in the 30 mg povorcitinib QD dose group, consistent with the published efficacy results. Notably, the genes impacted reflected JAK/STAT signaling transcripts downstream of TNF-α signaling, or those regulated by TGF-β. Proteomic analyses were conducted on blood samples obtained at baseline and Weeks 4 and 8 from patients receiving povorcitinib (15, 30, 60, or 90 mg) QD or placebo. Povorcitinib was associated with transcriptomic downregulation of multiple HS and inflammatory signaling markers as well as the reversal of gene expression previously associated with HS lesional and wounded skin. Povorcitinib also demonstrated dose-dependent modulation of several proteins implicated in HS pathophysiology, with changes observed by Week 4. The reversal of HS lesional gene signatures and rapid, dose-dependent protein regulation highlight the potential of JAK1 inhibition to modulate underlying disease pathology in HS.
Keywords: INCB054707; JAK1; hidradenitis suppurativa; inflammatory skin diseases; povorcitinib; proteomics; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
H.L., L.L.S. and S.H.S. are employees and shareholders of Incyte Research Institute/Incyte Corporation. Incyte was involved in the design of the study; the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; and in writing the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of the oral Janus kinase 1 inhibitor povorcitinib (INCB054707) in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa in a phase 2, randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging, placebo-controlled study.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024 Mar;90(3):521-529. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.034. Epub 2023 Oct 21. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 37871805 Clinical Trial.
-
Janus kinase 1 inhibitor INCB054707 for patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa: results from two phase II studies.Br J Dermatol. 2022 May;186(5):803-813. doi: 10.1111/bjd.20969. Epub 2022 Mar 6. Br J Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34978076 Free PMC article.
-
Pilot study of topical ruxolitinib demonstrates efficacy and blunting of heterogeneous inflammatory processes in mild hidradenitis suppurativa.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Apr 28;192(5):845-856. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae495. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39708369 Clinical Trial.
-
Janus-kinase inhibitors in dermatology: A review of their use in psoriasis, vitiligo, systemic lupus erythematosus, hidradenitis suppurativa, dermatomyositis, lichen planus, lichen planopilaris, sarcoidosis and graft-versus-host disease.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2023 [SEASON];90(1):30-40. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_15_2023. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2023. PMID: 38031699 Review.
-
Hidradenitis Suppurativa and JAK Inhibitors: A Review of the Published Literature.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Apr 20;59(4):801. doi: 10.3390/medicina59040801. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37109759 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comorbidities, Clinical Presentation, Subtypes, and Treatment of HS Patients in Lithuania.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 3;13(13):3900. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133900. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38999466 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Therapeutic Targets in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Focusing on HIF-1α, Nrf2, STATs, and RORγt.Curr Drug Targets. 2025;26(8):507-533. doi: 10.2174/0113894501372670250408074908. Curr Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 40247798 Review.
-
Rethinking Hidradenitis Suppurativa Management: Insights into Bacterial Interactions and Treatment Evolution.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Mar 17;13(3):268. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030268. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
European S2k guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa part 2: Treatment.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025 May;39(5):899-941. doi: 10.1111/jdv.20472. Epub 2024 Dec 19. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025. PMID: 39699926 Free PMC article.
-
IRAK4 Targeting: A Breakthrough Approach to Combat Hidradenitis Suppurativa.Biologics. 2025 Jun 30;19:387-397. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S525106. eCollection 2025. Biologics. 2025. PMID: 40621493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frew J.W., Lowes M.A., Goldfarb N., Butt M., Piguet V., O’Brien E., Ingram J., Jemec G.B.E., Tan J., Zouboulis C., et al. Global harmonization of morphological definitions in hidradenitis suppurativa for a proposed glossary. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:449–455. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.5467. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frew J.W., Marzano A.V., Wolk K., Join-Lambert O., Alavi A., Lowes M.A., Piguet V. A systematic review of promising therapeutic targets in hidradenitis suppurativa: A critical evaluation of mechanistic and clinical relevance. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021;141:316–324.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2020.06.019. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

