Whole-Transcriptome Sequencing of Antler Tissue Reveals That circRNA2829 Regulates Chondrocyte Proliferation and Differentiation via the miR-4286-R+1/FOXO4 Axis
- PMID: 37108365
- PMCID: PMC10139046
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087204
Whole-Transcriptome Sequencing of Antler Tissue Reveals That circRNA2829 Regulates Chondrocyte Proliferation and Differentiation via the miR-4286-R+1/FOXO4 Axis
Abstract
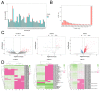
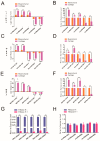
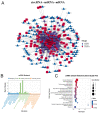
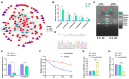
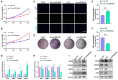
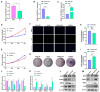
The antler is the unique mammalian organ found to be able to regenerate completely and periodically after loss, and the continuous proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal cells and chondrocytes together complete the regeneration of the antler. Circular non-coding RNAs (circRNAs) are considered to be important non-coding RNAs that regulate body development and growth. However, there are no reports on circRNAs regulating the antler regeneration process. In this study, full-transcriptome high-throughput sequencing was performed on sika deer antler interstitial and cartilage tissues, and the sequencing results were verified and analyzed. The competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network related to antler growth and regeneration was further constructed, and the differentially expressed circRNA2829 was screened out from the network to study its effect on chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. The results indicated that circRNA2829 promoted cell proliferation and increased the level of intracellular ALP. The analysis of RT-qPCR and Western blot demonstrated that the mRNA and protein expression levels of genes involved in differentiation rose. These data revealed that circRNAs play a crucial regulatory role in deer antler regeneration and development. CircRNA2829 might regulate the antler regeneration process through miR-4286-R+1/FOXO4.
Keywords: FOXO4; RNA sequencing; antler; ceRNAs; circRNA2829; miR-4286-R+1; sika deer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
METTL3/YTHDC1-medicated m6A modification of circRNA3634 regulates the proliferation and differentiation of antler chondrocytes by miR-124486-5-MAPK1 axis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Dec 7;28(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00515-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 38062349 Free PMC article.
-
NSUN2/ALYREF-medicated m5C-modified circRNA505 regulates the proliferation, differentiation, and glycolysis of antler chondrocytes via the miRNA-127/p53 axis and LDHA.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;309(Pt 1):142527. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.142527. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40147663
-
Full-length transcriptome and microRNA sequencing reveal the specific gene-regulation network of velvet antler in sika deer with extremely different velvet antler weight.Mol Genet Genomics. 2019 Apr;294(2):431-443. doi: 10.1007/s00438-018-1520-8. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Mol Genet Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30539301
-
Exploring the mechanisms regulating regeneration of deer antlers.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2004 May 29;359(1445):809-22. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2004.1471. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15293809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deer antler--a novel model for studying organ regeneration in mammals.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Nov;56:111-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.07.007. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25046387 Review.
Cited by
-
METTL3/YTHDC1-medicated m6A modification of circRNA3634 regulates the proliferation and differentiation of antler chondrocytes by miR-124486-5-MAPK1 axis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Dec 7;28(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00515-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 38062349 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead box O proteins in chondrocyte aging and diseases.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Aug 10;54:167-179. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.07.011. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 40822516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNA in cartilage regeneration: regulatory mechanism and therapeutic strategies.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 26;13:1522303. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1522303. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40206827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma exosomal miR-122-5p_R-1, miR-23b-3p_R + 1, and miR-15a-5p_R-1 are associated with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Aug 25;25(1):1063. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11487-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40855526 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

