Lipid-Independent Regulation of PLIN5 via IL-6 through the JAK/STAT3 Axis in Hep3B Cells
- PMID: 37108378
- PMCID: PMC10138877
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087219
Lipid-Independent Regulation of PLIN5 via IL-6 through the JAK/STAT3 Axis in Hep3B Cells
Abstract
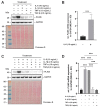
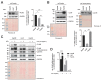
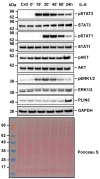
Perilipin 5 (PLIN5) is a lipid droplet coat protein that is highly expressed in oxidative tissues such as those of muscles, the heart and the liver. PLIN5 expression is regulated by a family of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and modulated by the cellular lipid status. So far, research has focused on the role of PLIN5 in the context of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and specifically in lipid droplet formation and lipolysis, where PLIN5 serves as a regulator of lipid metabolism. In addition, there are only limited studies connecting PLIN5 to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), where PLIN5 expression is proven to be upregulated in hepatic tissue. Considering that HCC development is highly driven by cytokines present throughout NAFLD development and in the tumor microenvironment, we here explore the possible regulation of PLIN5 by cytokines known to be involved in HCC and NAFLD progression. We demonstrate that PLIN5 expression is strongly induced by interleukin-6 (IL-6) in a dose- and time-dependent manner in Hep3B cells. Moreover, IL-6-dependent PLIN5 upregulation is mediated by the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway, which can be blocked by transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Furthermore, IL-6-mediated PLIN5 upregulation changes when IL-6 trans-signaling is stimulated through the addition of soluble IL-6R. In sum, this study sheds light on lipid-independent regulation of PLIN5 expression in the liver, making PLIN5 a crucial target for NAFLD-induced HCC.
Keywords: HCC; IL-6; JAK/STAT3; NAFLD; NASH; cytokines; fat metabolism; perilipin; transforming growth factor-β; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Understanding the Role of Perilipin 5 in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Its Role in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review of Novel Insights.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 17;22(10):5284. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105284. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34067931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of Perilipin 5 Protects Against Hepatic Injury in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Missing Inflammasome Activation.Cells. 2020 May 28;9(6):1346. doi: 10.3390/cells9061346. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32481590 Free PMC article.
-
Perilipin 5 Ameliorates Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation via SMAD2/3 and SNAIL Signaling Pathways and Suppresses STAT3 Activation.Cells. 2021 Aug 24;10(9):2184. doi: 10.3390/cells10092184. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571833 Free PMC article.
-
Perilipin 5 alleviates HCV NS5A-induced lipotoxic injuries in liver.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Apr 6;18(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1022-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 30954078 Free PMC article.
-
The ménage à trois of autophagy, lipid droplets and liver disease.Autophagy. 2022 Jan;18(1):50-72. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1895658. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 33794741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The influence of perilipin 5 deficiency on gut microbiome profiles in murine metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and MAFLD-hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Oct 14;14:1443654. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1443654. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39469452 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments.Open Med (Wars). 2025 Jun 9;20(1):20251215. doi: 10.1515/med-2025-1215. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40520339 Free PMC article.
-
Perilipin 5 deletion protects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Feb 22;10(1):94. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01860-4. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38388533 Free PMC article.
-
Plantaginis Semen Ameliorates Hyperuricemia Induced by Potassium Oxonate.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 5;25(15):8548. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158548. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126116 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

