Essential Oils from Mediterranean Plants Inhibit In Vitro Monocyte Adhesion to Endothelial Cells from Umbilical Cords of Females with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 37108387
- PMCID: PMC10138528
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087225
Essential Oils from Mediterranean Plants Inhibit In Vitro Monocyte Adhesion to Endothelial Cells from Umbilical Cords of Females with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
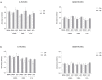
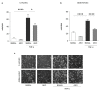
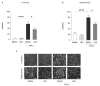
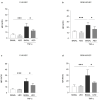
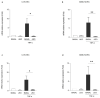
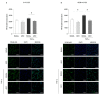
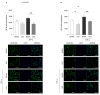
Essential oils (EOs) are mixtures of volatile compounds belonging to several chemical classes derived from aromatic plants using different distillation techniques. Recent studies suggest that the consumption of Mediterranean plants, such as anise and laurel, contributes to improving the lipid and glycemic profile of patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). Hence, the aim of the present study was to investigate the potential anti-inflammatory effect of anise and laurel EOs (AEO and LEO) on endothelial cells isolated from the umbilical cord vein of females with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM-HUVEC), which is a suitable in vitro model to reproduce the pro-inflammatory phenotype of a diabetic endothelium. For this purpose, the Gas Chromatographic/Mass Spectrometric (GC-MS) chemical profiles of AEO and LEO were first analyzed. Thus, GDM-HUVEC and related controls (C-HUVEC) were pre-treated for 24 h with AEO and LEO at 0.025% v/v, a concentration chosen among others (cell viability by MTT assay), and then stimulated with TNF-α (1 ng/mL). From the GC-MS analysis, trans-anethole (88.5%) and 1,8-cineole (53.9%) resulted as the major components of AEO and LEO, respectively. The results in C- and GDM-HUVEC showed that the treatment with both EOs significantly reduced: (i) the adhesion of the U937 monocyte to HUVEC; (ii) vascular adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) protein and gene expression; (iii) Nuclear Factor-kappa B (NF-κB) p65 nuclear translocation. Taken together, these data suggest the anti-inflammatory efficacy of AEO and LEO in our in vitro model and lay the groundwork for further preclinical and clinical studies to study their potential use as supplements to mitigate vascular endothelial dysfunction associated with DM.
Keywords: HUVEC; NF-κB p65; VCAM-1; anise; anti-inflammatory; diabetes; endothelial dysfunction; essential oils; inflammation; laurel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of adhesion molecule expression in human endothelial and smooth muscle cells by omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acids: involvement of the transcription factor NF-kappaB?Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2008 Jan;78(1):33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2007.10.004. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2008. PMID: 18036803
-
Essential Oil from Fructus Alpiniae Zerumbet Protects Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells In Vitro from Injury Induced by High Glucose Levels by Suppressing Nuclear Transcription Factor-Kappa B Signaling.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Oct 4;23:4760-4767. doi: 10.12659/msm.906463. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28976943 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin protects against vascular inflammation in mice and TNF-alpha-induced monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells via suppressing IΚBα/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Nutr Biochem. 2015 Mar;26(3):293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Dec 15. J Nutr Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25577468 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative Effects of Essential Oils on Diabetes Mellitus: A Review.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(26):2274-2287. doi: 10.2174/0115680266314922240822091215. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39225203 Review.
-
Essential Oils and Their Major Compounds in the Treatment of Chronic Inflammation: A Review of Antioxidant Potential in Preclinical Studies and Molecular Mechanisms.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Dec 23;2018:6468593. doi: 10.1155/2018/6468593. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30671173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardioprotective Peptides from Dry-Cured Ham in Primary Endothelial Cells and Human Plasma: An Omics Approach.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 24;14(7):772. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070772. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722877 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Endophyte Actinomycetota sp. JW0824 Strain as a Potential Bioinoculant to Enhance the Yield, Nutritive Value, and Chemical Composition of Different Cultivars of Anise (Pimpinella anisum L.) Seeds.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;13(8):553. doi: 10.3390/biology13080553. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raut J.S., Karuppayil S.M. A Status Review on the Medicinal Properties of Essential Oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014;62:250–264. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.05.055. - DOI
-
- Thalappil M.A., Butturini E., Carcereri de Prati A., Bettin I., Antonini L., Sapienza F.U., Garzoli S., Ragno R., Mariotto S. Pinus Mugo Essential Oil Impairs STAT3 Activation through Oxidative Stress and Induces Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2022;27:4834. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154834. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

