Extracellular Vesicles for Therapeutic Nucleic Acid Delivery: Loading Strategies and Challenges
- PMID: 37108446
- PMCID: PMC10139028
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087287
Extracellular Vesicles for Therapeutic Nucleic Acid Delivery: Loading Strategies and Challenges
Abstract
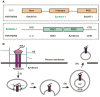
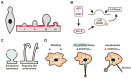
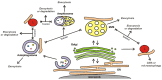
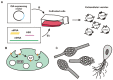
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane vesicles released into the extracellular milieu by cells of various origins. They contain different biological cargoes, protecting them from degradation by environmental factors. There is an opinion that EVs have a number of advantages over synthetic carriers, creating new opportunities for drug delivery. In this review, we discuss the ability of EVs to function as carriers for therapeutic nucleic acids (tNAs), challenges associated with the use of such carriers in vivo, and various strategies for tNA loading into EVs.
Keywords: apoptotic bodies; drug delivery; ectosomes; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; intraluminal vesicles; microvesicles; multivesicular body; nanocarrier; nucleic acid therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Transporters.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 17;24(12):10267. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210267. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles for drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Nov 15;106(Pt A):148-156. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.02.006. Epub 2016 Feb 27. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 26928656 Review.
-
Circulating Extracellular Vesicles As Biomarkers and Drug Delivery Vehicles in Cardiovascular Diseases.Biomolecules. 2021 Mar 5;11(3):388. doi: 10.3390/biom11030388. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33808038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles as novel drug delivery systems to target cancer and other diseases: Recent advancements and future perspectives.F1000Res. 2023 Mar 23;12:329. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.132186.1. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2023. PMID: 37868300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Strategies for Exosome Cargo Loading and Targeting Delivery.Cells. 2023 May 17;12(10):1416. doi: 10.3390/cells12101416. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles: key drivers of immunomodulation in breast cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 4;16:1548535. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1548535. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40103824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle mimetics as delivery vehicles for oligonucleotide-based therapeutics and plasmid DNA.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 17;12:1437817. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1437817. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39493304 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of Using Small Extracellular Vesicles as an Anti-Cancer Drug.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 14;24(18):14063. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814063. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 19;26(10):4835. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104835. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA and RNA Molecules as a Foundation of Therapy Strategies for Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 15;15(8):2141. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082141. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bost J.P., Barriga H., Holme M.N., Gallud A., Maugeri M., Gupta D., Lehto T., Valadi H., Esbjörner E.K., Stevens M.M., et al. Delivery of Oligonucleotide Therapeutics: Chemical Modifications, Lipid Nanoparticles, and Extracellular Vesicles. ACS Nano. 2021;15:13993–14021. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c05099. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

