Integration of mRNA and miRNA Analysis Reveals the Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Stress Response in Hemerocallis fulva
- PMID: 37108448
- PMCID: PMC10139057
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087290
Integration of mRNA and miRNA Analysis Reveals the Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Stress Response in Hemerocallis fulva
Abstract
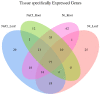
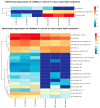
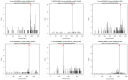
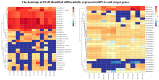
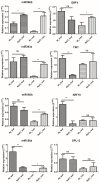
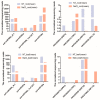
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) belong to non-coding small RNAs which have been shown to take a regulatory function at the posttranscriptional level in plant growth development and response to abiotic stress. Hemerocallis fulva is an herbaceous perennial plant with fleshy roots, wide distribution, and strong adaptability. However, salt stress is one of the most serious abiotic stresses to limit the growth and production of Hemerocallis fulva. To identify the miRNAs and their targets involved in the salt stress resistance, the salt-tolerant H. fulva with and without NaCl treatment were used as materials, and the expression differences of miRNAs-mRNAs related to salt-tolerance were explored and the cleavage sites between miRNAs and targets were also identified by using degradome sequencing technology. In this study, twenty and three significantly differential expression miRNAs (p-value < 0.05) were identified in the roots and leaves of H. fulva separately. Additionally, 12,691 and 1538 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were also obtained, respectively, in roots and leaves. Moreover, 222 target genes of 61 family miRNAs were validated by degradome sequencing. Among the DE miRNAs, 29 pairs of miRNA targets displayed negatively correlated expression profiles. The qRT-PCR results also showed that the trends of miRNA and DEG expression were consistent with those of RNA-seq. A gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of these targets revealed that the calcium ion pathway, oxidative defense response, microtubule cytoskeleton organization, and DNA binding transcription factor responded to NaCl stress. Five miRNAs, miR156, miR160, miR393, miR166, and miR396, and several hub genes, squamosa promoter-binding-like protein (SPL), auxin response factor 12 (ARF), transport inhibitor response 1-like protein (TIR1), calmodulin-like proteins (CML), and growth-regulating factor 4 (GRF4), might play central roles in the regulation of NaCl-responsive genes. These results indicate that non-coding small RNAs and their target genes that are related to phytohormone signaling, Ca2+ signaling, and oxidative defense signaling pathways are involved in H. fulva's response to NaCl stress.
Keywords: Hemerocallis fulva; NaCl treatment; degradome; differentially expressed gene; miRNA; posttranscriptional regulation; salt stress; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationship that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Mushtaq Z., Faizan S., Gulzar B. Salt stress, its impacts on plants and the strategies plants are employing against it: A review. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2020;8:81–91.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

