Otilonium Bromide Prevents Cholinergic Changes in the Distal Colon Induced by Chronic Water Avoidance Stress, a Rat Model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- PMID: 37108603
- PMCID: PMC10139220
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087440
Otilonium Bromide Prevents Cholinergic Changes in the Distal Colon Induced by Chronic Water Avoidance Stress, a Rat Model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Abstract
Irritable Bowel syndrome (IBS) is a highly widespread gastrointestinal disorder whose symptomatology mainly affect the large intestine. Among the risk factors, psychosocial stress is the most acknowledged. The repeated water avoidance stress (rWAS) is considered an animal model of psychosocial stress that is capable of mimicking IBS. Otilonium bromide (OB), which is orally administered, concentrates in the large bowel and controls most of the IBS symptoms in humans. Several reports have shown that OB has multiple mechanisms of action and cellular targets. We investigated whether the application of rWAS to rats induced morphological and functional alterations of the cholinergic neurotransmission in the distal colon and whether OB prevented them. The results demonstrated that rWAS affects cholinergic neurotransmission by causing an increase in acid mucin secretion, in the amplitude of electrically evoked contractile responses, abolished by atropine, and in the number of myenteric neurons expressing choline acetyltransferase. OB counteracted these changes and also showed an intrinsic antimuscarinic effect on the post-synaptic muscular receptors. We assume that the rWAS consequences on the cholinergic system are linked to corticotrophin-releasing factor-1 (CRF1) receptor activation by the CRF hypothalamic hormone. OB, by interfering with the CFR/CRFr activation, interrupted the cascade events responsible for the changes affecting the rWAS rat colon.
Keywords: atropine; choline acetyl transferase; contractile responses; corticotropin-releasing factor; methacholine; mucus secretion; muscarinic receptors; protein gene product 9.5; tetrodotoxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
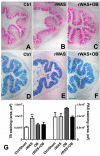
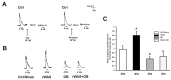
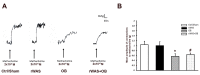
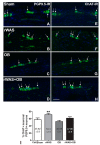
References
-
- Fond G., Loundou A., Hamdani N., Boukouaci W., Dargel J.O., Roger M., Tamouza R., Leboyer M., Boyer L. Anxiety and depression comorbidities in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2014;264:651–660. doi: 10.1007/s00406-014-0502-z. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

