Basic Pathogenic Mechanisms and Epigenetic Players Promoted by Extracellular Vesicles in Vascular Damage
- PMID: 37108672
- PMCID: PMC10138986
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087509
Basic Pathogenic Mechanisms and Epigenetic Players Promoted by Extracellular Vesicles in Vascular Damage
Abstract
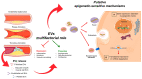
Both progression from the early pathogenic events to clinically manifest cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and cancer impact the integrity of the vascular system. Pathological vascular modifications are affected by interplay between endothelial cells and their microenvironment. Soluble factors, extracellular matrix molecules and extracellular vesicles (EVs) are emerging determinants of this network that trigger specific signals in target cells. EVs have gained attention as package of molecules with epigenetic reversible activity causing functional vascular changes, but their mechanisms are not well understood. Valuable insights have been provided by recent clinical studies, including the investigation of EVs as potential biomarkers of these diseases. In this paper, we review the role and the mechanism of exosomal epigenetic molecules during the vascular remodeling in coronary heart disease as well as in cancer-associated neoangiogenesis.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; biomarkers; cancer; exosome; extracellular vesicle; vascular damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles: An Epigenetic View of the Cancer Microenvironment.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:649161. doi: 10.1155/2015/649161. Epub 2015 Oct 25. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26582468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of Extracellular Vesicles in Vascular-Related Functions in Cancer Progression and Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 26;20(10):2584. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102584. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31130715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles contribute to tumor microenvironment remodeling.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Jun 25;20(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00904-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35752798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles and Cellular Communication in Metastasis.Cells. 2021 Dec 6;10(12):3429. doi: 10.3390/cells10123429. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for cancer.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Jan 1;318(1):C29-C39. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00280.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31693397 Review.
Cited by
-
The translational potential of miR-26 in atherosclerosis and development of agents for its target genes ACC1/2, COL1A1, CPT1A, FBP1, DGAT2, and SMAD7.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Jan 9;23(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02119-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38195542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epitranscriptome: A Novel Regulatory Layer during Atherosclerosis Progression.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(15):2915-2930. doi: 10.2174/0109298673322775240822051304. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39219432 Review.
-
Evolving Strategies for Extracellular Vesicles as Future Cardiac Therapeutics: From Macro- to Nano-Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 4;25(11):6187. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116187. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircRNA_012164/MicroRNA-9-5p axis mediates cardiac fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 23;19(7):e0302772. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302772. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39042659 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Atherosclerosis: State of the Art.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 27;25(1):388. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010388. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203558 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Napoli C., D’Armiento F.P., Mancini F.P., Postiglione A., Witztum J.L., Palumbo G., Palinski W. Fatty streak formation occurs in human fetal aortas and is greatly enhanced by maternal hypercholesterolemia. Intimal accumulation of low density lipoprotein and its oxidation precede monocyte recruitment into early atherosclerotic lesions. J. Clin. Investig. 1997;100:2680–2690. doi: 10.1172/JCI119813. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Napoli C., Glass C.K., Witztum J.L., Deutsch R., D’Armiento F.P., Palinski W. Influence of maternal hypercholesterolaemia during pregnancy on progression of early atherosclerotic lesions in childhood: Fate of early lesions in children (FELIC) study. Lancet. 1999;354:1234–1241. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)02131-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

