Characterization of Porcine Ocular Surface Epithelial Microenvironment
- PMID: 37108705
- PMCID: PMC10145510
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087543
Characterization of Porcine Ocular Surface Epithelial Microenvironment
Abstract
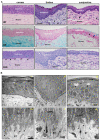
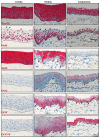
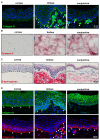
The porcine ocular surface is used as a model of the human ocular surface; however, a detailed characterization of the porcine ocular surface has not been documented. This is due, in part, to the scarcity of antibodies produced specifically against the porcine ocular surface cell types or structures. We performed a histological and immunohistochemical investigation on frozen and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded ocular surface tissue from domestic pigs using a panel of 41 different antibodies related to epithelial progenitor/differentiation phenotypes, extracellular matrix and associated molecules, and various niche cell types. Our observations suggested that the Bowman's layer is not evident in the cornea; the deep invaginations of the limbal epithelium in the limbal zone are analogous to the limbal interpalisade crypts of human limbal tissue; and the presence of goblet cells in the bulbar conjunctiva. Immunohistochemistry analysis revealed that the epithelial progenitor markers cytokeratin (CK)15, CK14, p63α, and P-cadherin were expressed in both the limbal and conjunctival basal epithelium, whereas the basal cells of the limbal and conjunctival epithelium did not stain for CK3, CK12, E-cadherin, and CK13. Antibodies detecting marker proteins related to the extracellular matrix (collagen IV, Tenascin-C), cell-matrix adhesion (β-dystroglycan, integrin α3 and α6), mesenchymal cells (vimentin, CD90, CD44), neurons (neurofilament), immune cells (HLA-ABC; HLA-DR, CD1, CD4, CD14), vasculature (von Willebrand factor), and melanocytes (SRY-homeobox-10, human melanoma black-45, Tyrosinase) on the normal human ocular surface demonstrated similar immunoreactivity on the normal porcine ocular surface. Only a few antibodies (directed against N-cadherin, fibronectin, agrin, laminin α3 and α5, melan-A) appeared unreactive on porcine tissues. Our findings characterize the main immunohistochemical properties of the porcine ocular surface and provide a morphological and immunohistochemical basis useful to research using porcine models. Furthermore, the analyzed porcine ocular structures are similar to those of humans, confirming the potential usefulness of pig eyes to study ocular surface physiology and pathophysiology.
Keywords: conjunctiva; cornea; extracellular matrix; limbal epithelial progenitor cells; limbal niche cells; limbal stem cells; melanocytes; porcine ocular surface.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Characterization of extracellular matrix components in the limbal epithelial stem cell compartment.Exp Eye Res. 2007 Dec;85(6):845-60. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.08.020. Epub 2007 Sep 2. Exp Eye Res. 2007. PMID: 17927980
-
A single cell atlas of human cornea that defines its development, limbal progenitor cells and their interactions with the immune cells.Ocul Surf. 2021 Jul;21:279-298. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2021.03.010. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Ocul Surf. 2021. PMID: 33865984 Free PMC article.
-
Histological and immunohistochemical characterization of the porcine ocular surface.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 13;15(1):e0227732. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227732. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31929592 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of limbal stem cells.Exp Eye Res. 2005 Sep;81(3):247-64. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.02.016. Exp Eye Res. 2005. PMID: 16051216 Review.
-
Limbal stem cells of the corneal epithelium.Surv Ophthalmol. 2000 Mar-Apr;44(5):415-25. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6257(00)00109-0. Surv Ophthalmol. 2000. PMID: 10734241 Review.
Cited by
-
A detailed survey of the murine limbus, its stem cell distribution, and its boundaries with the cornea and conjunctiva.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2024 Oct 10;13(10):1015-1027. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szae055. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39077915 Free PMC article.
-
Stable topical application of antimicrobials using plumbing rings in an ex vivo porcine corneal infection model.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 3;20(4):e0319911. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319911. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40179321 Free PMC article.
-
Postmortal epithelial changes of donor corneas impair applicability of a refractive ultraviolet femtosecond laser.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 12;15(1):5198. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89867-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39939419 Free PMC article.
-
A practical and safer model of nitrogen mustard injury in cornea.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 3;20(7):e0327622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327622. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40608742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shortt A.J., Secker G.A., Munro P.M., Khaw P.T., Tuft S.J., Daniels J.T. Characterization of the Limbal Epithelial Stem Cell Niche: Novel Imaging Techniques Permit in Vivo Observation and Targeted Biopsy of Limbal Epithelial Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2007;25:1402–1409. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2006-0580. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

