Identification and Functional Analysis of foxo Genes in Chinese Tongue Sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis)
- PMID: 37108789
- PMCID: PMC10142177
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087625
Identification and Functional Analysis of foxo Genes in Chinese Tongue Sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis)
Abstract
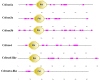
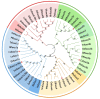
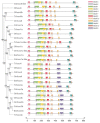
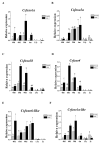
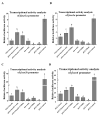
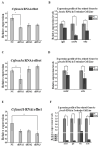
The Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis) is a traditional, precious fish in China. Due to the large growth difference between males and females, the investigation of their sex determination and differentiation mechanisms receives a great deal of attention. Forkhead Box O (FoxO) plays versatile roles in the regulation of sex differentiation and reproduction. Our recent transcriptomic analysis has shown that foxo genes may participate in the male differentiation and spermatogenesis of Chinese tongue sole. In this study, six Csfoxo members (Csfoxo1a, Csfoxo3a, Csfoxo3b, Csfoxo4, Csfoxo6-like, and Csfoxo1a-like) were identified. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that these six members were clustered into four groups corresponding to their denomination. The expression patterns of the gonads at different developmental stages were further analyzed. All members showed high levels of expression in the early stages (before 6 months post-hatching), and this expression was male-biased. In addition, promoter analysis found that the addition of C/EBPα and c-Jun transcription factors enhanced the transcriptional activities of Csfoxo1a, Csfoxo3a, Csfoxo3b, and Csfoxo4. The siRNA-mediated knockdown of the Csfoxo1a, Csfoxo3a, and Csfoxo3b genes in the testicular cell line of Chinese tongue sole affected the expression of genes related to sex differentiation and spermatogenesis. These results have broadened the understanding of foxo's function and provide valuable data for studying the male differentiation of tongue sole.
Keywords: Cynoglossus semilaevis; foxo; promoter activity; siRNA knockdown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization and functional analysis of the GATA4 in tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis).Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Mar;193:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2015.12.001. Epub 2015 Dec 5. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26667142
-
Cloning and functional analysis of c/ebpα as negative regulator of dmrt1 in Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis).Gene. 2021 Feb 5;768:145321. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145321. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Gene. 2021. PMID: 33221538
-
Molecular characterization and expression profiles of GATA6 in tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis).Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Aug;198:19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27040526
-
Cloning, expression and functional analysis of the desert hedgehog (dhh) gene in Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis).Gene Expr Patterns. 2021 Mar;39:119163. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2020.119163. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Gene Expr Patterns. 2021. PMID: 33359643
-
The Role of the Heat Shock Cognate Protein 70 Genes in Sex Determination and Differentiation of Chinese Tongue Sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 13;24(4):3761. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043761. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835170 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

