SOX2-Sensing: Insights into the Role of SOX2 in the Generation of Sensory Cell Types in Vertebrates
- PMID: 37108798
- PMCID: PMC10141063
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087637
SOX2-Sensing: Insights into the Role of SOX2 in the Generation of Sensory Cell Types in Vertebrates
Abstract
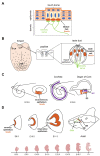
The SOX2 transcription factor is a key regulator of nervous system development, and its mutation in humans leads to a rare disease characterized by severe eye defects, cognitive defects, hearing defects, abnormalities of the CNS and motor control problems. SOX2 has an essential role in neural stem cell maintenance in specific regions of the brain, and it is one of the master genes required for the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells. Sox2 is expressed in sensory organs, and this review will illustrate how it regulates the differentiation of sensory cell types required for hearing, touching, tasting and smelling in vertebrates and, in particular, in mice.
Keywords: SOX2; hear; sensory; smell; taste; touch; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deconstructing Sox2 Function in Brain Development and Disease.Cells. 2022 May 10;11(10):1604. doi: 10.3390/cells11101604. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35626641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sox2 conditional mutation in mouse causes ataxic symptoms, cerebellar vermis hypoplasia, and postnatal defects of Bergmann glia.Glia. 2018 Sep;66(9):1929-1946. doi: 10.1002/glia.23448. Epub 2018 May 6. Glia. 2018. PMID: 29732603
-
MicroRNA-145 Regulates Neural Stem Cell Differentiation Through the Sox2-Lin28/let-7 Signaling Pathway.Stem Cells. 2016 May;34(5):1386-95. doi: 10.1002/stem.2309. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Stem Cells. 2016. PMID: 26849971
-
More than just Stem Cells: Functional Roles of the Transcription Factor Sox2 in Differentiated Glia and Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 13;20(18):4540. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184540. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31540269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOS Rescues Neuronal Differentiation of Sox2-Deleted Neural Stem Cells by Genome-Wide Regulation of Common SOX2 and AP1(FOS-JUN) Target Genes.Cells. 2021 Jul 12;10(7):1757. doi: 10.3390/cells10071757. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34359927 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
SOX2 and NR2F1 coordinate the gene expression program of the early postnatal visual thalamus.Biol Open. 2025 Aug 15;14(8):bio062014. doi: 10.1242/bio.062014. Epub 2025 Aug 1. Biol Open. 2025. PMID: 40631402 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

