In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation of Posaconazole-Amphotericin B Combination against Candida albicans: In Vitro Interacting Concentrations Are Associated with In Vivo Free Drug Levels
- PMID: 37108889
- PMCID: PMC10146624
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9040434
In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation of Posaconazole-Amphotericin B Combination against Candida albicans: In Vitro Interacting Concentrations Are Associated with In Vivo Free Drug Levels
Abstract
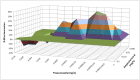
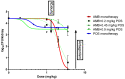
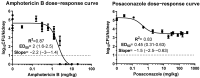
The in vitro/in vivo correlation of antifungal combination testing is necessary in order to assess the efficacy of combination regimens. We, therefore, attempted to correlate in vitro chequerboard testing of posaconazole (POS) and amphotericin B (AMB) with the in vivo outcome of combination therapy against experimental candidiasis in a neutropenic murine model. The AMB + POS combination was tested against a Candida albicans isolate. In vitro, a broth microdilution 8 × 12 chequerboard method with serial two-fold drug dilutions was used. In vivo, CD1 female neutropenic mice with experimental disseminated candidiasis were treated with i.p. AMB and p.o. POS alone and in combination at three effective doses (ED20, ED50 and ED80 corresponding to 20%, 50% and 80% of maximal effect, respectively). CFU/kidneys after 2 days were determined. The pharmacodynamic interactions were assessed based on Bliss independence interaction analysis. In vitro, a Bliss antagonism of -23% (-23% to -22%) was observed at 0.03-0.125 mg/L of AMB with 0.004-0.015 mg/L of POS, while a Bliss synergy of 27% (14%-58%) was observed at 0.008-0.03 mg/L of AMB with 0.000015-0.001 mg/L of POS. In vivo, Bliss synergy (13 ± 4%) was found when an AMB ED20 of 1 mg/kg was combined with all POS ED 0.2-0.9 mg/kg, while Bliss antagonism (35-83%) was found for the combinations of AMB ED50 2 mg/kg and ED80 3.2 mg/kg with POS ED80 of 0.9 mg/kg. Free drug serum levels of POS and AMB in in vivo synergistic and antagonistic combinations were correlated with the in vitro synergistic and antagonistic concentrations, respectively. Both synergistic and antagonistic interactions were found for the AMB + POS combination. POS compromised the efficacy of high effective AMB doses and enhanced low ineffective AMB doses. In vitro concentration-dependent interactions were correlated with in vivo dose-dependent interactions of the AMB + POS combination. In vivo interactions occurred at free drug serum levels close to in vitro interacting concentrations.
Keywords: Candida albicans; amphotericin B; combination therapy; in vitro–in vivo correlation; posaconazole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synergistic effect of pyrvinium pamoate and posaconazole against Cryptococcus neoformans in vitro and in vivo.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Dec 9;12:1074903. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1074903. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36569209 Free PMC article.
-
[Short communication: In vitro activity of amphotericin B with fluconazole or voriconazole combinations against Candida albicans isolates].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2008 Jan;42(1):149-55. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2008. PMID: 18444574 Turkish.
-
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic comparison of amphotericin B (AMB) and two lipid-associated AMB preparations, liposomal AMB and AMB lipid complex, in murine candidiasis models.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Feb;50(2):674-84. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.2.674-684.2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16436726 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter Collaborative Study of the Interaction of Antifungal Combinations against Candida Spp. by Loewe Additivity and Bliss Independence-Based Response Surface Analysis.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Sep 16;8(9):967. doi: 10.3390/jof8090967. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36135692 Free PMC article.
-
[In vitro synergistic effect of moxifloxacin and amphotericin B combination against Candida strains].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2010 Jan;44(1):65-70. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2010. PMID: 20455400 Turkish.
Cited by
-
Effects of fluconazole and amphotericin B in the control of cryptococcal pneumonia in vivo.AMB Express. 2025 Jan 30;15(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13568-025-01827-3. AMB Express. 2025. PMID: 39885057 Free PMC article.
-
CAF to the Rescue! Potential and Challenges of Combination Antifungal Therapy for Reducing Morbidity and Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Serious Fungal Infections.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 30;11(11):ofae646. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae646. eCollection 2024 Nov. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39544494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marr K. Combination antifungal therapy: Where are we now, and where are we going? Oncology. 2004;18:24–29. - PubMed
-
- Meletiadis J., Mouton J.W., Meis J.F.G.M., Verweij P.E. Methodological issues related to antifungal drug interaction modelling for filamentous fungi. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 2003;13:101–117. doi: 10.1097/00013542-200207000-00002. - DOI
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute . M27-A3: Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts; Approved Standard. 3rd ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; Wayne, PA, USA: 2008.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

