Early and Late Response and Glucocorticoid-Sparing Effect of Belimumab in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Joint and Skin Manifestations: Results from the Belimumab in Real Life Setting Study-Joint and Skin (BeRLiSS-JS)
- PMID: 37109077
- PMCID: PMC10146447
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13040691
Early and Late Response and Glucocorticoid-Sparing Effect of Belimumab in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Joint and Skin Manifestations: Results from the Belimumab in Real Life Setting Study-Joint and Skin (BeRLiSS-JS)
Abstract
Aim: To assess the efficacy of belimumab in joint and skin manifestations in a nationwide cohort of patients with SLE.
Methods: All patients with skin and joint involvement enrolled in the BeRLiSS cohort were considered. Belimumab (intravenous, 10 mg/kg) effectiveness in joint and skin manifestations was assessed by DAS28 and CLASI, respectively. Attainment and predictors of DAS28 remission (<2.6) and LDA (≥2.6, ≤3.2), CLASI = 0, 1, and improvement in DAS28 and CLASI indices ≥20%, ≥50%, and ≥70% were evaluated at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months.
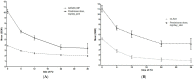
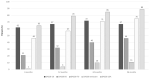
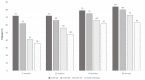
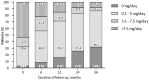
Results: DAS28 < 2.6 was achieved by 46%, 57%, and 71% of patients at 6, 12, and 24 months, respectively. CLASI = 0 was achieved by 36%, 48%, and 62% of patients at 6, 12, and 24 months, respectively. Belimumab showed a glucocorticoid-sparing effect, being glucocorticoid-free at 8.5%, 15.4%, 25.6%, and 31.6% of patients at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months, respectively. Patients achieving DAS-LDA and CLASI-50 at 6 months had a higher probability of remission at 12 months compared with those who did not (p = 0.034 and p = 0.028, respectively).
Conclusions: Belimumab led to clinical improvement in a significant proportion of patients with joint or skin involvement in a real-life setting and was associated with a glucocorticoid-sparing effect. A significant proportion of patients with a partial response at 6 months achieved remission later on during follow-up.
Keywords: Cutaneous LE Area and Severity Index (CLASI); belimumab; disease activity score (DAS)-28; low disease activity; remission; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nikoloudaki M., Nikolopoulos D., Koutsoviti S., Flouri I., Kapsala N., Repa A., Katsimbri P., Theotikos E., Pitsigavdaki S., Pateromichelaki K., et al. Clinical response trajectories and drug persistence in systemic lupus erythematosus patients on belimumab treatment: A real-life, multicentre observational study. Front. Immunol. 2023;13:1074044. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1074044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trentin F., Gatto M., Zen M., Maddalena L., Nalotto L., Saccon F., Zanatta E., Iaccarino L., Doria A. Effectiveness, Tolerability, and Safety of Belimumab in Patients with Refractory SLE: A Review of Observational Clinical-Practice-Based Studies. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018;54:331–343. doi: 10.1007/s12016-018-8675-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iaccarino L., Andreoli L., Bocci E.B., Bortoluzzi A., Ceccarelli F., Conti F., De Angelis R., De Marchi G., De Vita S., Di Matteo A., et al. Clinical predictors of response and discontinuation of belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in real life setting. Results of a large, multicentric, nationwide study. J. Autoimmun. 2018;86:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.09.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Iaccarino L., Bettio S., Reggia R., Zen M., Frassi M., Andreoli L., Gatto M., Piantoni S., Nalotto L., Franceschini F., et al. Effects of belimumab on flare rate and expected damage progression in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. 2017;69:115–123. doi: 10.1002/acr.22971. - DOI - PubMed

