Protein Induced by Vitamin K Absence II: A Potential Biomarker to Differentiate Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma from Pancreatic Benign Lesions and Predict Vascular Invasion
- PMID: 37109105
- PMCID: PMC10147026
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12082769
Protein Induced by Vitamin K Absence II: A Potential Biomarker to Differentiate Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma from Pancreatic Benign Lesions and Predict Vascular Invasion
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly malignant gastrointestinal tumor with a poor prognosis. Serum biomarker carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) was the only well-established biomarker for PDAC with inadequate efficacy. This present study aimed to determine the ability of PIVKA-II to discriminate PDAC from pancreatic benign lesions and predict vascular invasion preoperatively.
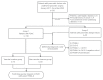
Methods: Patients who underwent pancreatic surgery from 2017 to 2020 were enrolled. We examined the differential diagnostic ability of protein induced by vitamin K absence II (PIVKA-II), CA19-9, and their combination and 138 with PDAC evaluated the predictive value of PIVKA-II for vascular invasion in PDAC.
Methods: A total of 138 patients with PDAC and 90 patients with pancreatic benign lesions who underwent pancreatic surgery from 2017 to 2020 were enrolled. The clinicopathological characteristics were recorded.
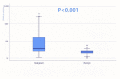
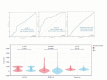
Results: There was a significant difference in levels of serum PIVKA-II between PDAC patients and patients with pancreatic benign lesions (p < 0.001). When the cut-off value was set to 28.9 mAU/mL according to the ROCs, the AUC, sensitivity, and specificity of PIVKA-II were 0.787, 68.1%, and 83.3%, respectively. The combined PIVKA-II and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) enhanced the diagnostic accuracy, and the AUC, sensitivity, and specificity were 0.945, 87.7%, and 94.4%, respectively. PIVKA-II > 36.4 mAU/mL were independent predictive factors of vascular invasion in PDAC (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: PIVKA-II was a potential diagnostic biomarker to differentiate PDAC from pancreatic benign lesions. PIVKA-II was complementary to CA19-9, and the combination enhanced the differential diagnostic performance. PIVKA-II > 36.4 mAU/mL was an independent predictive factor of vascular invasion in PDAC.
Keywords: biomarker; diagnosis; pancreatic cancer; protein induced by vitamin K absence II; vascular invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Combined PIVKA II and Vimentin-Guided EMT Tracking in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Combined Biomarker-Guided EMT Tracking in PDAC.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 27;16(13):2362. doi: 10.3390/cancers16132362. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001424 Free PMC article.
-
PIVKA-II: A biomarker for diagnosing and monitoring patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2021 May 20;16(5):e0251656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251656. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34015010 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
CA19-9, CEA and PIVKA-Ⅱ as a novel panel of serum markers for diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.Clin Biochem. 2025 Jun;137:110902. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2025.110902. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Clin Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40024361
-
Diagnostic value of serum PIVKA-II levels for BCLC early hepatocellular carcinoma and correlation with HBV DNA.Cancer Biomark. 2018;23(2):235-242. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181402. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 30103302
-
Current status of targeted microbubbles in diagnostic molecular imaging of pancreatic cancer.Bioeng Transl Med. 2020 Sep 7;6(1):e10183. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10183. eCollection 2021 Jan. Bioeng Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33532585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging horizons on molecular and circulating biomarkers in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Nov 7;14:1483306. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1483306. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39575418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined PIVKA II and Vimentin-Guided EMT Tracking in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Combined Biomarker-Guided EMT Tracking in PDAC.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 27;16(13):2362. doi: 10.3390/cancers16132362. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001424 Free PMC article.
-
PANC-1 Cell Line as an Experimental Model for Characterizing PIVKA-II Production, Distribution, and Molecular Mechanisms Leading to Protein Release in PDAC.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 20;25(6):3498. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063498. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542466 Free PMC article.
-
Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis: Serum Biomarkers and the Potential for Aptamer-Based Biosensors.Molecules. 2025 Apr 30;30(9):2012. doi: 10.3390/molecules30092012. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40363817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma with conventional ultrasound, Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasound, and biochemical indicator: a multicenter study.Insights Imaging. 2024 Oct 28;15(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01743-3. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39466459 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

