Genetic Ablation and Pharmacological Blockade of Bradykinin B1 Receptor Unveiled a Detrimental Role for the Kinin System in Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 37109224
- PMCID: PMC10144326
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12082888
Genetic Ablation and Pharmacological Blockade of Bradykinin B1 Receptor Unveiled a Detrimental Role for the Kinin System in Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
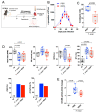
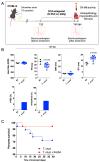
Chagas disease, the parasitic infection caused by Trypanosoma cruzi, afflicts about 6 million people in Latin America. Here, we investigated the hypothesis that T. cruzi may fuel heart parasitism by activating B1R, a G protein-coupled (brady) kinin receptor whose expression is upregulated in inflamed tissues. Studies in WT and B1R-/- mice showed that T. cruzi DNA levels (15 days post infection-dpi) were sharply reduced in the transgenic heart. FACS analysis revealed that frequencies of proinflammatory neutrophils and monocytes were diminished in B1R-/- hearts whereas CK-MB activity (60 dpi) was exclusively detected in B1R+/+ sera. Since chronic myocarditis and heart fibrosis (90 dpi) were markedly attenuated in the transgenic mice, we sought to determine whether a pharmacological blockade of the des-Arg9-bradykinin (DABK)/B1R pathway might alleviate chagasic cardiomyopathy. Using C57BL/6 mice acutely infected by a myotropic T. cruzi strain (Colombian), we found that daily treatment (15-60 dpi) with R-954 (B1R antagonist) reduced heart parasitism and blunted cardiac injury. Extending R-954 treatment to the chronic phase (120-160 dpi), we verified that B1R targeting (i) decreased mortality indexes, (ii) mitigated chronic myocarditis, and (iii) ameliorated heart conduction disturbances. Collectively, our study suggests that a pharmacological blockade of the proinflammatory KKS/DABK/B1R pathway is cardioprotective in acute and chronic Chagas disease.
Keywords: Chagas disease; GPCRs; Trypanosoma cruzi; bradykinin; kallikrein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mast Cell Coupling to the Kallikrein-Kinin System Fuels Intracardiac Parasitism and Worsens Heart Pathology in Experimental Chagas Disease.Front Immunol. 2017 Aug 2;8:840. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00840. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28824610 Free PMC article.
-
Trypanosoma cruzi induces edematogenic responses in mice and invades cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells in vitro by activating distinct kinin receptor (B1/B2) subtypes.FASEB J. 2003 Jan;17(1):73-5. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0477fje. Epub 2002 Nov 1. FASEB J. 2003. PMID: 12424228
-
Interactions between carboxypeptidase M and kinin B1 receptor in endothelial cells.Inflamm Res. 2019 Oct;68(10):845-855. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01264-6. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 31218444
-
[Chagasic myocardiopathy: historical perspective].Medicina (B Aires). 1999;59 Suppl 2:25-40. Medicina (B Aires). 1999. PMID: 10668240 Review. Spanish.
-
G Protein-Coupled Kinin Receptors and Immunity Against Pathogens.Adv Immunol. 2017;136:29-84. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Adv Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28950949 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Pathways and Pathophysiological Implications of Viral Infection-Driven Activation of Kallikrein-Kinin System (KKS).Viruses. 2024 Feb 3;16(2):245. doi: 10.3390/v16020245. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38400022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models for exploring Chagas disease pathogenesis and supporting drug discovery.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024 Dec 10;37(4):e0015523. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00155-23. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39545730 Review.
References
-
- Nunes M.C.P., Beaton A., Acquatella H., Bern C., Bolger A.F., Echeverria L.E., Dutra W.O., Gascon J., Morillo C.A., Oliveira-Filho J., et al. Chagas Cardiomyopathy: An Update of Current Clinical Knowledge and Management: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;138:e169–e209. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000599. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro Dos Santos R., Rassi S., Feitosa G., Grecco O.T., Rassi A., Jr., da Cunha A.B., de Carvalho V.B., Guarita-Souza L.C., de Oliveira W., Jr., Tura B.R., et al. Cell therapy in Chagas cardiomyopathy (Chagas arm of the multicenter randomized trial of cell therapy in cardiopathies study): A multicenter randomized trial. Circulation. 2012;125:2454–2461. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.067785. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

