Spectrophotometric Investigations of Charge Transfer Complexes of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors with Iodine as a σ-Electron Acceptor: Application to Development of Universal High-Throughput Microwell Assay for Their Determination in Pharmaceutical Formulations
- PMID: 37109733
- PMCID: PMC10143458
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59040775
Spectrophotometric Investigations of Charge Transfer Complexes of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors with Iodine as a σ-Electron Acceptor: Application to Development of Universal High-Throughput Microwell Assay for Their Determination in Pharmaceutical Formulations
Abstract
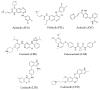
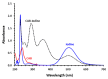
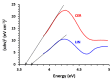
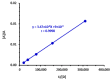
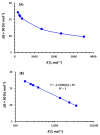
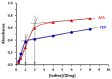
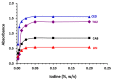
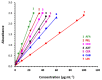
Background and Objective: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are used for the treatment of different types of cancers. The current study describes, for the first time, the ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometric investigation of charge transfer complexes (CTCs) of seven TKIs, as electron donors, and iodine, as σ-electron. Materials and Methods: The formation of CTCs was promoted in dichloromethane, among the other solvents used in the investigation. The molar absorptivity values, association constants, and free energy changes of the CTCs were determined. Stoichiometric ratio of TKI: iodine as well as TKIs site(s) of interaction were addressed. Reaction was the basis for constructing a novel simple and accurate 96-microwell spectrophotometric assay (MW-SPA) with high-throughput property for the quantitative determination of TKIs in their pharmaceutical formulations. Results: Beer's law, which relates CTC absorbances to TKI concentrations, was followed within the optimal range of 2 to 100 µg/well (r ranged from 0.9991 to 0.9998). Detection and quantification limits ranged from 0.91 to 3.60 and 2.76 to 10.92 g µmL-1, respectively. Relative standard deviations values for the intra- and inter-assay precisions of the proposed MW-SPA did not exceed 2.13 and 2.34%, respectively. Studies of recovery demonstrated MW-SPA accuracy, with results ranging from 98.9% to 102.4%. All TKIs, both in bulk form and in pharmaceutical formulations (tablets), were effectively determined using the suggested MW-SPA. Conclusions: The current MW-SPA involved a simple procedure and it was convenient as it could analyse all proposed TKIs utilizing a single assay system at once measuring wavelengths for all TKIs. In addition, the proposed MW-SPA has high throughput which enables the processing of a batch of huge samples' number in very short reasonable time period. In conclusion, TKIs can be routinely analysed in their dosage forms in quality control laboratories, and the assay can be highly valuable and helpful in this regard.
Keywords: 96-Microwell spectrophotometric assay; Iodine; charge-transfer complex; high-throughput analysis; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spectrophotometric and computational investigations of charge transfer complexes of chloranilic acid with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and application to development of novel universal 96-microwell assay for their determination in pharmaceutical formulations.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021 May 5;252:119482. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.119482. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021. PMID: 33571740
-
Experimental and Computational Evaluation of Chloranilic Acid as an Universal Chromogenic Reagent for the Development of a Novel 96-Microwell Spectrophotometric Assay for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.Molecules. 2021 Jan 31;26(3):744. doi: 10.3390/molecules26030744. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33572664 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Green and High Throughput Microplate Reader-Assisted Universal Microwell Spectrophotometric Assay for Direct Determination of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Their Pharmaceutical Formulations Irrespective the Diversity of Their Chemical Structures.Molecules. 2023 May 12;28(10):4049. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104049. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241790 Free PMC article.
-
A One-Step Green Microwell Spectrophotometric Assay for the Determination of Certain New Chemotherapeutic Drug Formulations.J AOAC Int. 2024 Nov 1;107(6):903-911. doi: 10.1093/jaoacint/qsae052. J AOAC Int. 2024. PMID: 38941505
-
Charge Transfer Complex of Lorlatinib with Chloranilic Acid: Characterization and Application to the Development of a Novel 96-Microwell Spectrophotometric Assay with High Throughput.Molecules. 2023 May 1;28(9):3852. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093852. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175262 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Spectrophotometric and computational characterization of charge transfer complex of selumetinib with 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone and its utilization in developing an innovative green and high throughput microwell assay for analysis of bulk form and pharmaceutical formulation.BMC Chem. 2025 Jan 29;19(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01353-6. BMC Chem. 2025. PMID: 39881370 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrophotometric Study of Charge-Transfer Complexes of Ruxolitinib with Chloranilic Acid and 2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone: An Application to the Development of a Green and High-Throughput Microwell Method for Quantification of Ruxolitinib in Its Pharmaceutical Formulations.Molecules. 2023 Nov 30;28(23):7877. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237877. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization, Geneva, Report 3 February 2022. [(accessed on 2 April 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer.
-
- Prager G.W., Braga S., Bystricky B., Qvortrup C., Criscitiello C., Esin E., Sonke G.S., Martínez G.A., Frenel J.-S., Karamouzis M., et al. Global cancer control: Responding to the growing burden, rising costs and inequalities in access. ESMO Open. 2018;3:e000285. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000285. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

