Is the Novel Slot Blot a Useful Method for Quantification of Intracellular Advanced Glycation End-Products?
- PMID: 37110222
- PMCID: PMC10144988
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo13040564
Is the Novel Slot Blot a Useful Method for Quantification of Intracellular Advanced Glycation End-Products?
Abstract
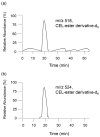
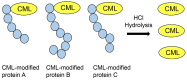
Various types of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) have been identified and studied. I have reported a novel slot blot analysis to quantify two types of AGEs, glyceraldehyde-derived AGEs, also called toxic AGEs (TAGE), and 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose AGEs. The traditional slot blot method has been used for the detection and quantification of RNA, DNA, and proteins since around 1980 and is one of the more commonly used analog technologies to date. However, the novel slot blot analysis has been used to quantify AGEs from 2017 to 2022. Its characteristics include (i) use of a lysis buffer containing tris-(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane, urea, thiourea, and 3-[3-(cholamidopropyl)-dimetyl-ammonio]-1-propane sulfonate (a lysis buffer with a composition similar to that used in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis-based proteomics analysis); (ii) probing of AGE-modified bovine serum albumin (e.g., standard AGE aliquots); and (iii) use of polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. In this review, the previously used quantification methods of slot blot, western blot, immunostaining, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (MS), matrix-associated laser desorption/ionization-MS, and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-MS are described. Lastly, the advantages and disadvantages of the novel slot blot compared to the above methods are discussed.
Keywords: 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)-dimethyl-ammonio]-1-propane sulfonate; Tris; advanced glycation end products; enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; gas chromatography–mass spectrometry; liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–mass spectrometry; polyvinylidene difluoride membrane; slot blot; thiourea; urea.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Mastrocola R., Collino M., Nigro D., Chiazza F., D’Antona G., Aragno M., Minetto M. Accumulation of Advanced Glycation End-Products and Activation of the SCAP/SREBP Lipogenetic Pathway Occur in Diet-Induced Obese Mouse Skeletal Muscle. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0119587. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119587. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang G., Yeh Y., Chen W., Ko Y., Pang J.S., Lee H. Inhibition of Advanved Glycation End-Products Formation Attenuates Cardiac Electrical and Mechanical Remodeling and Vulnerability to Tachyarrthmias in Diabetic Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019;368:66–78. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.252080. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

