Thanksgiving to Yeast, the HMGB Proteins History from Yeast to Cancer
- PMID: 37110415
- PMCID: PMC10142021
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11040993
Thanksgiving to Yeast, the HMGB Proteins History from Yeast to Cancer
Abstract
Yeasts have been a part of human life since ancient times in the fermentation of many natural products used for food. In addition, in the 20th century, they became powerful tools to elucidate the functions of eukaryotic cells as soon as the techniques of molecular biology developed. Our molecular understandings of metabolism, cellular transport, DNA repair, gene expression and regulation, and the cell division cycle have all been obtained through biochemistry and genetic analysis using different yeasts. In this review, we summarize the role that yeasts have had in biological discoveries, the use of yeasts as biological tools, as well as past and on-going research projects on HMGB proteins along the way from yeast to cancer.
Keywords: HMGB proteins; cancer; interactome; molecular methods; research hits; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
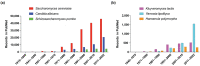

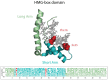
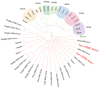
References
-
- Goffeau A. The Yeast Genome. Pathol. Biol. 1998;46:96–97. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

