Suppressing Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Gene Expression and Replication by RNase P Ribozyme
- PMID: 37110852
- PMCID: PMC10142857
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28083619
Suppressing Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Gene Expression and Replication by RNase P Ribozyme
Abstract
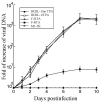
Kaposi's sarcoma, an AIDS-defining illness, is caused by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), an oncogenic virus. In this study, we engineered ribozymes derived from ribonuclease P (RNase P) catalytic RNA with targeting against the mRNA encoding KSHV immediate early replication and transcription activator (RTA), which is vital for KSHV gene expression. The functional ribozyme F-RTA efficiently sliced the RTA mRNA sequence in vitro. In cells, KSHV production was suppressed with ribozyme F-RTA expression by 250-fold, and RTA expression was suppressed by 92-94%. In contrast, expression of control ribozymes hardly affected RTA expression or viral production. Further studies revealed both overall KSHV early and late gene expression and viral growth decreased because of F-RTA-facilitated suppression of RTA expression. Our results indicate the first instance of RNase P ribozymes having potential for use in anti-KSHV therapy.
Keywords: Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus; RNase P; antiviral; catalytic RNA; gene therapy; herpesvirus; ribozyme.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Roizman B., Pellett P.E. The family herpesviridae: A brief introduction. In: Knipe D.M., Howley P.M., editors. Fields Virology. Volume 2. Lippincott-William & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2001. pp. 2381–2398.
-
- Ganem D. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. In: Knipe D.M., Howley P.M., Griffin D.E., Martin M.A., Lamb R.A., Roizman B., Straus S.E., editors. Fields Virology. Lippincott-William & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2007. pp. 2820–2845.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

