Nanostructures Stacked on Hafnium Oxide Films Interfacing Graphene and Silicon Oxide Layers as Resistive Switching Media
- PMID: 37110908
- PMCID: PMC10146930
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13081323
Nanostructures Stacked on Hafnium Oxide Films Interfacing Graphene and Silicon Oxide Layers as Resistive Switching Media
Abstract
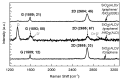
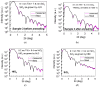
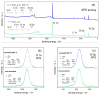
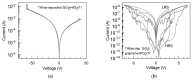
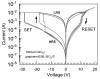
SiO2 films were grown to thicknesses below 15 nm by ozone-assisted atomic layer deposition. The graphene was a chemical vapor deposited on copper foil and transferred wet-chemically to the SiO2 films. On the top of the graphene layer, either continuous HfO2 or SiO2 films were grown by plasma-assisted atomic layer deposition or by electron beam evaporation, respectively. Micro-Raman spectroscopy confirmed the integrity of the graphene after the deposition processes of both the HfO2 and SiO2. Stacked nanostructures with graphene layers intermediating the SiO2 and either the SiO2 or HfO2 insulator layers were devised as the resistive switching media between the top Ti and bottom TiN electrodes. The behavior of the devices was studied comparatively with and without graphene interlayers. The switching processes were attained in the devices supplied with graphene interlayers, whereas in the media consisting of the SiO2-HfO2 double layers only, the switching effect was not observed. In addition, the endurance characteristics were improved after the insertion of graphene between the wide band gap dielectric layers. Pre-annealing the Si/TiN/SiO2 substrates before transferring the graphene further improved the performance.
Keywords: atomic layer deposition; graphene; hafnium oxide; resistive switching; silicon oxide; stacked nanostructures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Sun K., Chen J., Yan X.M. The future of memristors: Materials engineering and neural networks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2006773. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202006773. - DOI
-
- Niu Y., Yu X., Dong X., Zheng D., Liu S., Gan Z., Chang K., Liu B., Jiang K., Li Y., et al. Improved Al2O3 RRAM performance based on SiO2/MoS2 quantum dots hybrid structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2022;120:022106. doi: 10.1063/5.0070400. - DOI
-
- Kahro T., Castán H., Dueñas S., Merisalu J., Kozlova J., Jõgiaas T., Piirsoo H.-M., Kasikov A., Ritslaid P., Mändar H., et al. Structure and behavior of ZrO2-graphene-ZrO2 stacks. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A. 2020;38:063411. doi: 10.1116/6.0000390. - DOI
-
- Kahro T., Tarre A., Käämbre T., Piirsoo H.-M., Kozlova J., Ritslaid P., Kasikov A., Jõgiaas T., Vinuesa G., Dueñas S., et al. Hafnium Oxide/Graphene/Hafnium Oxide-Stacked Nanostructures as Resistive Switching Media. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021;4:5152–5163. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.1c00587. - DOI
-
- Zhang R., Chang K.-C., Chang T.-C., Tsai T.-M., Chen K.-H., Lou J.-C., Chen J.-H., Young T.F., Shih C.-C., Yang Y.-L., et al. High performance of graphene oxide-doped silicon oxide-based resistance random access memory. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013;8:497. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-8-497. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

