Serum Interleukin 6, Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score and Phase Angle in Patients with Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 37111172
- PMCID: PMC10146872
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15081953
Serum Interleukin 6, Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score and Phase Angle in Patients with Crohn's Disease
Abstract
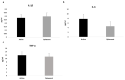
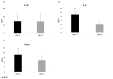
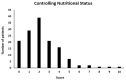
Crohn's disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that may occur in any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Asymptomatic or untreated inflammation along with malnutrition can often coexist in patients with CD, impairing clinical outcomes, therefore the aim of this study was to assess the relationship between inflammation, malnutrition risk and nutritional status in CD patients. Consecutive adult CD outpatients aged 18-65 years were recruited. Disease activity was clinically defined by the Crohn's Disease Activity Index (CDAI), whilst anthropometry and phase angle (PhA) were measured. The Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score was retrospectively calculated for screening malnutrition risk and blood samples were taken. A total of 140 CD patients with a mean age of 38.8 ± 13.9 years and an average weight of 64.9 ± 12.0 kg were included. Serum interleukin (IL)-6 concentration was increased in active-CD patients, unrelated to medical treatment, which was associated with CDAI and PhA. Based on the CONUT score, the prevalence of patients with moderate/severe malnutrition risk (score ≥ 5) was 10%, showing lower age, body mass index and fat mass, but higher IL-6 and IL-1β levels than subjects classified as not at risk (score 0-1). Finally, increased IL-6 levels and reduced PhA values were identified as independent predictors of moderate/severe malnutrition risk (p < 0.05). In conclusion, IL-6 increased in active-CD patients, which was inversely correlated with PhA. Although the CONUT score might be helpful for identifying CD patients at moderate/severe risk of malnutrition, larger studies are needed to verify these results in different settings.
Keywords: CONUT score; c reactive protein; inflammatory bowel disease; malnutrition; phase angle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of bioelectrical phase angle as a predictor of nutritional status in patients with Crohn's disease: A cross sectional study.Clin Nutr. 2020 May;39(5):1564-1571. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.06.023. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31303525
-
Prognostic significance of the Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score in predicting postoperative complications in patients with Crohn's disease.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 4;10(1):19040. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76115-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33149221 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional status and bioelectrical phase angle assessment in adult Crohn disease patients receiving anti-TNFα therapy.Dig Liver Dis. 2017 May;49(5):495-499. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2016.12.026. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Dig Liver Dis. 2017. PMID: 28096060
-
Cannabis for the treatment of Crohn's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 8;11(11):CD012853. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012853.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30407616 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score and the risk of mortality or impaired physical function in stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023 Aug;33(8):1501-1510. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2023.05.012. Epub 2023 May 12. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023. PMID: 37336716
Cited by
-
Association of systemic immune-inflammation index with malnutrition among Chinese hospitalized patients: a nationwide, multicenter, cross-sectional study.Front Nutr. 2024 Aug 27;11:1375053. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1375053. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39257607 Free PMC article.
-
Association of bioelectrical impedance phase angle and nutritional status in patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 16;12:1554535. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1554535. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40740641 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid profiles, disease activity, and protein intake in adult patients with Crohn's disease.Front Nutr. 2023 Oct 3;10:1245574. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1245574. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37854352 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin and HMW Oligomers in Relation to Inflammatory Markers in Crohn's Disease Patients.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 23;13(2):273. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020273. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002687 Free PMC article.
-
Phase Angle Predicts Malnutrition Risk and 6-month Mortality in Older Patients with Multimorbidity: A Retrospective Study.Clin Interv Aging. 2025 Jun 26;20:895-902. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S518795. eCollection 2025. Clin Interv Aging. 2025. PMID: 40599689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castiglione F., Imperatore N., Testa A., De Palma G.D., Nardone O.M., Pellegrini L., Caporaso N., Rispo A. One-Year Clinical Outcomes with Biologics in Crohn’s Disease: Transmural Healing Compared with Mucosal or No Healing. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2019;49:1026–1039. doi: 10.1111/apt.15190. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rispo A., Imperatore N., Testa A., Mainenti P., De Palma G.D., Luglio G., Maurea S., Nardone O.M., Caporaso N., Castiglione F. Bowel Damage in Crohn’s Disease: Direct Comparison of Ultrasonography-Based and Magnetic Resonance-Based Lemann Index. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017;23:143–151. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000980. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nikolaus S., Waetzig G.H., Butzin S., Ziolkiewicz M., Al-Massad N., Thieme F., Lövgren U., Rasmussen B.B., Reinheimer T.M., Seegert D., et al. Evaluation of Interleukin-6 and Its Soluble Receptor Components SIL-6R and Sgp130 as Markers of Inflammation in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2018;33:927–936. doi: 10.1007/s00384-018-3069-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

