Effectiveness of Positive Deviance Approach to Reduce Malnutrition among under Five Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Interventional Studies
- PMID: 37111180
- PMCID: PMC10143095
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15081961
Effectiveness of Positive Deviance Approach to Reduce Malnutrition among under Five Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Interventional Studies
Abstract
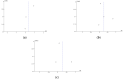
The high malnutrition rate in children under five makes this problem one of the public health problems. Various efforts have been made to reduce malnutrition in children under five, one of which is the implementation of community programs with a positive deviance approach which is considered an effective way because the solution to the problem comes from the local community. Thus, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the effect of interventions with a positive deviance approach to reducing under-five children's malnutrition. Systematic searches were conducted using the following journal databases: Science Direct, Pubmed, Proquest, SAGE journal, Web of Science, and Scopus. The article was included if using an intervention design. Data analysis used Review Manager 5.4 software, random effect model, outcome mean of difference, and 95% confidence interval. There were no significant differences between the intervention and control groups on the length for age z-scores (LAZ), weight for age z-scores (WAZ), and weight for height z-scores (WHZ) indicators. There was an increase in LAZ, WAZ, and WHZ scores in the intervention group, with a greater z-score than in the control group. In conclusion, interventions with the positive deviance approach can be used as an alternative to improving the nutritional status of under-five children. However, further research is needed to determine the effective duration of interventions in improving the nutritional status of children.
Keywords: malnutrition; positive deviance; stunting; under-five children; wasting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



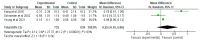
References
-
- WHO Stunting Prevalence among Children under 5 Years of Age.Pdf. [(accessed on 6 October 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/indicators/indicator-details/GHO/gho-j....
-
- UNICEF. WHO. World Bank . Levels and Trends Child Malnutrition: Key Findings of the 2020 Edition of the Joint Child Malnutrition Estimate. Volume 24. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020. pp. 1–16.
-
- Olofin I., McDonald C.M., Ezzati M., Flaxman S., Black R.E., Fawzi W.W., Caulfield L.E., Danaei G., Adair L., Arifeen S., et al. Associations of Suboptimal Growth with All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in Children under Five Years: A Pooled Analysis of Ten Prospective Studies. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e64636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064636. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

