Reduced Cholesterol Levels during Acute Human Babesiosis
- PMID: 37111499
- PMCID: PMC10144092
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12040613
Reduced Cholesterol Levels during Acute Human Babesiosis
Abstract
Background: Babesiosis, an intra-erythrocytic protozoan disease, is an emerging zoonotic parasitic disease worldwide. Cholesterol levels are correlated with severe infections, such as sepsis and COVID-19, and anecdotal reports suggest that high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol declines during acute babesiosis. Our aim was to describe the cholesterol levels in patients with acute babesiosis diagnosed in an endemic area in New York, hypothesizing that HDL levels correlate with the severity of infection.
Methods: We reviewed the medical records of adult patients with babesiosis diagnosed by identification of Babesia parasites on a thin blood smear and confirmed by polymerase chain reaction from 2013 to 2018, who also had available a lipid profile drawn at the time of clinical presentation. Additional lipid profile levels were considered as "baseline" if they were drawn within 2 months before or after the infection as part of routine care.
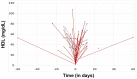
Results: A total of 39 patients with babesiosis had a lipid profile drawn on presentation. The patients were divided into two groups for comparison based on the treating physician's clinical decision: 33 patients who were admitted to the hospital and 8 patients who were evaluated as outpatients. A history of hypertension was more common in admitted patients (37% vs. 17%, p = 0.02). The median levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and HDL were significantly reduced in admitted patients compared to non-admitted patients (46 vs. 76 mg/dL, p = 0.04; and 9 vs. 28.5 mg/dL, p = 0.03, respectively). In addition, LDL and HDL levels returned to baseline values following resolution of acute babesiosis.
Conclusion: LDL and HDL levels are significantly reduced during acute babesiosis, suggesting that cholesterol depletion may predict disease severity. Pathogen and host factors may contribute to a reduction in serum cholesterol levels during acute babesiosis.
Keywords: Babesia; cholesterol; high-density lipoprotein; lipids; low-density lipoprotein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

