A Time-of-Flight Image Sensor Using 8-Tap P-N Junction Demodulator Pixels
- PMID: 37112329
- PMCID: PMC10143804
- DOI: 10.3390/s23083987
A Time-of-Flight Image Sensor Using 8-Tap P-N Junction Demodulator Pixels
Abstract
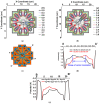
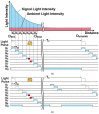
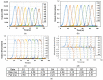
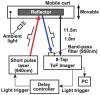
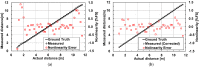
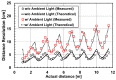
This paper presents a time-of-flight image sensor based on 8-Tap P-N junction demodulator (PND) pixels, which is designed for hybrid-type short-pulse (SP)-based ToF measurements under strong ambient light. The 8-tap demodulator implemented with multiple p-n junctions used for modulating the electric potential to transfer photoelectrons to eight charge-sensing nodes and charge drains has an advantage of high-speed demodulation in large photosensitive areas. The ToF image sensor implemented using 0.11 µm CIS technology, consisting of an 120 (H) × 60 (V) image array of the 8-tap PND pixels, successfully works with eight consecutive time-gating windows with the gating width of 10 ns and demonstrates for the first time that long-range (>10 m) ToF measurements under high ambient light are realized using single-frame signals only, which is essential for motion-artifact-free ToF measurements. This paper also presents an improved depth-adaptive time-gating-number assignment (DATA) technique for extending the depth range while having ambient-light canceling capability and a nonlinearity error correction technique. By applying these techniques to the implemented image sensor chip, hybrid-type single-frame ToF measurements with depth precision of maximally 16.4 cm (1.4% of the maximum range) and the maximum non-linearity error of 0.6% for the full-scale depth range of 1.0-11.5 m and operations under direct-sunlight-level ambient light (80 klux) have been realized. The depth linearity achieved in this work is 2.5 times better than that of the state-of-the-art 4-tap hybrid-type ToF image sensor.
Keywords: PN-junction demodulator (PND); depth precision; depth-adaptive time-gating-number assignment (DATA); image sensor; time-of-flight (ToF).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Niclass C., Soga M., Matsubara H., Ogawa M., Kagami M. A 0.18mm CMOS SoC for a 100-m-Range 10-Frame/s 200 96-Pixel Time-of-Flight Depth Sensor. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits. 2014;49:315–330. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2013.2284352. - DOI
-
- Kao Y.-H., Chu T.-S. A Direct-Sampling Pulsed Time-of-Flight Radar with Frequency-Defined Vernier Digital-to-Time Converter in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits. 2015;50:2665–2677. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2472599. - DOI
-
- Perenzoni M., Perenzoni D., Stoppa D. A 64 × 64-Pixels Digital Silicon Photomultiplier Direct TOF Sensor With 100-MPhotons/s/pixel Background Rejection and Imaging/Altimeter Mode With 0.14% Precision Up To 6 km for Spacecraft Navigation and Landing. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits. 2017;52:151–160. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2623635. - DOI
-
- Yoshioka K., Kubota H., Fukushima T., Kondo S., Ta T.T., Okuni H., Watanabe K., Hirono M., Ojima Y., Kimura K., et al. A 20-ch TDC/ADC Hybrid Architecture LiDAR SoC for 240×96 Pixel 200-m Range Imaging with Smart Accumulation Technique and Residue Quantizing SAR ADC. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits. 2018;53:3026–3038. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2868315. - DOI
-
- Zhang C., Lindner S., Antolovic I.M., Pavia J.M., Wolf M., Charbon E. 30-frames/s, 252 × 144 SPAD Flash LiDAR with 1728 Dual-Clock 48.8-ps TDCs, and Pixel-Wise Integrated Histogramming. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits. 2019;54:1137–1151. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2883720. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

