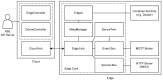
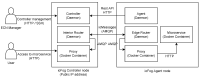
Performance Evaluation of Container Orchestration Tools in Edge Computing Environments
- PMID: 37112349
- PMCID: PMC10143384
- DOI: 10.3390/s23084008
Performance Evaluation of Container Orchestration Tools in Edge Computing Environments
Abstract
Edge computing is a viable approach to improve service delivery and performance parameters by extending the cloud with resources placed closer to a given service environment. Numerous research papers in the literature have already identified the key benefits of this architectural approach. However, most results are based on simulations performed in closed network environments. This paper aims to analyze the existing implementations of processing environments containing edge resources, taking into account the targeted quality of service (QoS) parameters and the utilized orchestration platforms. Based on this analysis, the most popular edge orchestration platforms are evaluated in terms of their workflow that allows the inclusion of remote devices in the processing environment and their ability to adapt the logic of the scheduling algorithms to improve the targeted QoS attributes. The experimental results compare the performance of the platforms and show the current state of their readiness for edge computing in real network and execution environments. These findings suggest that Kubernetes and its distributions have the potential to provide effective scheduling across the resources on the network's edge. However, some challenges still have to be addressed to completely adapt these tools for such a dynamic and distributed execution environment as edge computing implies.
Keywords: Internet of Things (IoT); K3s; KubeEdge; Kubernetes; container; edge computing; ioFog; service orchestration; service scheduling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
QoS-Based Service-Time Scheduling in the IoT-Edge Cloud.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Aug 28;21(17):5797. doi: 10.3390/s21175797. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34502688 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Scheduling of Contextually Categorised Internet of Things Services in Fog Computing Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 8;22(2):465. doi: 10.3390/s22020465. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062426 Free PMC article.
-
Local Scheduling in KubeEdge-Based Edge Computing Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 30;23(3):1522. doi: 10.3390/s23031522. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36772562 Free PMC article.
-
Cloud-Native Workload Orchestration at the Edge: A Deployment Review and Future Directions.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 16;23(4):2215. doi: 10.3390/s23042215. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36850813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Edge-Computing Architectures for Internet of Things Applications: A Survey.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Nov 11;20(22):6441. doi: 10.3390/s20226441. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33187267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient Network Slicing with SDN and Heuristic Algorithm for Low Latency Services in 5G/B5G Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 30;23(13):6053. doi: 10.3390/s23136053. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37447902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Čilić I., Podnar Žarko I. Adaptive Data-Driven Routing for Edge-to-Cloud Continuum: A Content-Based Publish/Subscribe Approach; Proceedings of the Internet of Things; Dublin, Ireland. 20–23 June 2022; Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2022. pp. 29–42.
-
- OpenFog Consortium . OpenFog Reference Architecture for Fog Computing. OpenFog Consortium; Fremont, CA, USA: 2017.
-
- Rodriguez M.A., Buyya R. Container-based cluster orchestration systems: A taxonomy and future directions. Softw.-Pract. Exp. 2019;49:698–719. doi: 10.1002/spe.2660. - DOI
-
- Oleghe O. Container Placement and Migration in Edge Computing: Concept and Scheduling Models. IEEE Access. 2021;9:68028–68043. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3077550. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources