Longitudinal Gait Analysis of a Transfemoral Amputee Patient: Single-Case Report from Socket-Type to Osseointegrated Prosthesis
- PMID: 37112378
- PMCID: PMC10143735
- DOI: 10.3390/s23084037
Longitudinal Gait Analysis of a Transfemoral Amputee Patient: Single-Case Report from Socket-Type to Osseointegrated Prosthesis
Abstract
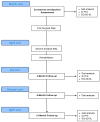
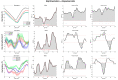
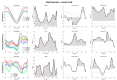
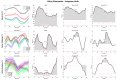
The aim of the present case report was to provide a longitudinal functional assessment of a patient with transfemoral amputation from the preoperative status with socket-type prosthesis to one year after the osseointegration surgery. A 44 years-old male patient was scheduled for osseointegration surgery 17 years after transfemoral amputation. Gait analysis was performed through 15 wearable inertial sensors (MTw Awinda, Xsens) before surgery (patient wearing his standard socket-type prosthesis) and at 3-, 6-, and 12-month follow-ups after osseointegration. ANOVA in Statistical Parametric Mapping was used to assess the changes in amputee and sound limb hip and pelvis kinematics. The gait symmetry index progressively improved from the pre-op with socket-type (1.14) to the last follow-up (1.04). Step width after osseointegration surgery was half of the pre-op. Hip flexion-extension range significantly improved at follow-ups while frontal and transverse plane rotations decreased (p < 0.001). Pelvis anteversion, obliquity, and rotation also decreased over time (p < 0.001). Spatiotemporal and gait kinematics improved after osseointegration surgery. One year after surgery, symmetry indices were close to non-pathological gait and gait compensation was sensibly decreased. From a functional point of view, osseointegration surgery could be a valid solution in patients with transfemoral amputation facing issues with traditional socket-type prosthesis.
Keywords: biomechanics; case report; gait analysis; gait symmetry; osseointegration; socket-type; transfemoral amputation; wearable sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gait rehabilitation for a patient with an osseointegrated prosthesis following transfemoral amputation.Physiother Theory Pract. 2017 Feb;33(2):147-161. doi: 10.1080/09593985.2016.1265620. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Physiother Theory Pract. 2017. PMID: 28045571
-
Osseointegrated Prosthetic Implants for People With Lower-Limb Amputation: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2019 Dec 12;19(7):1-126. eCollection 2019. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2019. PMID: 31911825 Free PMC article.
-
Osseointegrated prostheses improve balance and balance confidence in individuals with unilateral transfemoral limb loss.Gait Posture. 2023 Feb;100:132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2022.12.011. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Gait Posture. 2023. PMID: 36521257
-
Osseointegrated prostheses for rehabilitation following amputation : The pioneering Swedish model.Unfallchirurg. 2017 Apr;120(4):285-292. doi: 10.1007/s00113-017-0331-4. Unfallchirurg. 2017. PMID: 28229193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Functional rehabilitation after transfemoral amputation : Shaft prosthesis or endo-exo prosthesis?].Unfallchirurg. 2022 Apr;125(4):266-274. doi: 10.1007/s00113-022-01148-1. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Unfallchirurg. 2022. PMID: 35212810 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Inertial Measuring System to Evaluate Gait Parameters and Dynamic Alignments for Lower-Limb Amputation Subjects.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 26;24(5):1519. doi: 10.3390/s24051519. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475055 Free PMC article.
-
Wearing Time, Quality of Life, and Complications of Lower Limb Bone-anchored Prostheses: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025 Aug 5;13(8):e7041. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000007041. eCollection 2025 Aug. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025. PMID: 40765680 Free PMC article.
-
Lower Extremity Osseointegration Postoperative Rehabilitation Protocols: A Scoping Review.Phys Ther. 2025 Jan 8;105(1):pzae139. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzae139. Phys Ther. 2025. PMID: 39385465 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

