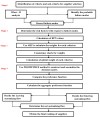
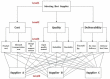
Multicriteria Decision Making in Supply Chain Management Using FMEA and Hybrid AHP-PROMETHEE Algorithms
- PMID: 37112382
- PMCID: PMC10146861
- DOI: 10.3390/s23084041
Multicriteria Decision Making in Supply Chain Management Using FMEA and Hybrid AHP-PROMETHEE Algorithms
Abstract
In today's global environment, supplier selection is one of the critical strategic decisions made by supply chain management. The supplier selection process involves the evaluation of suppliers based on several criteria, including their core capabilities, price offerings, lead times, geographical proximity, data collection sensor networks, and associated risks. The ubiquitous presence of internet of things (IoT) sensors at different levels of supply chains can result in risks that cascade to the upstream end of the supply chain, making it imperative to implement a systematic supplier selection methodology. This research proposes a combinatorial approach for risk assessment in supplier selection using the failure mode effect analysis (FMEA) with hybrid analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and the preference ranking organization method for enrichment evaluation (PROMETHEE). The FMEA is used to identify the failure modes based on a set of supplier criteria. The AHP is implemented to determine the global weights for each criterion, and PROMETHEE is used to prioritize the optimal supplier based on the lowest supply chain risk. The integration of multicriteria decision making (MCDM) methods overcomes the shortcomings of the traditional FMEA and enhances the precision of prioritizing the risk priority numbers (RPN). A case study is presented to validate the combinatorial model. The outcomes indicate that suppliers were evaluated more effectively based on company chosen criteria to select a low-risk supplier over the traditional FMEA approach. This research establishes a foundation for the application of multicriteria decision-making methodology for unbiased prioritization of critical supplier selection criteria and evaluation of different supply chain suppliers.
Keywords: analytical hierarchy process (AHP); failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA); internet of things (IoT) sensors; preference ranking organization method for enrichment evaluation (PROMETHEE); supply chain risk management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated Multicriteria Decision-Making Methods to Solve Supplier Selection Problem: A Case Study in a Hospital.J Healthc Eng. 2019 Oct 10;2019:5614892. doi: 10.1155/2019/5614892. eCollection 2019. J Healthc Eng. 2019. PMID: 31687120 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Model for Building Material Supplier Selection Based on Entropy-AHP Weighted TOPSIS.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Feb 24;22(2):259. doi: 10.3390/e22020259. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33286032 Free PMC article.
-
A Multicriteria Decision-Making Framework for Access Point Selection in Hybrid LiFi/WiFi Networks Using Integrated AHP-VIKOR Technique.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 23;23(3):1312. doi: 10.3390/s23031312. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36772352 Free PMC article.
-
Green Supplier Selection Based on Green Practices Evaluated Using Fuzzy Approaches of TOPSIS and ELECTRE with a Case Study in a Chinese Internet Company.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 7;17(9):3268. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17093268. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32392876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the Best Supplier Selection Criteria in Supply Chain Management During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Front Psychol. 2022 Apr 29;12:804954. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.804954. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35572841 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Risk assessment of crane operation hazards using modified FMEA approach with Z-number and set pair analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 26;10(9):e28603. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28603. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38726143 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging Nanomanufacturing and Artificial Intelligence-A Comprehensive Review.Materials (Basel). 2024 Apr 2;17(7):1621. doi: 10.3390/ma17071621. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38612135 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Handfield R.B., Graham G., Burns L. Corona virus, tariffs, trade wars and supply chain evolutionary design. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2020;40:1649–1660. doi: 10.1108/IJOPM-03-2020-0171. - DOI
-
- Ghadge A., Wurtmann H., Seuring S. Managing climate change risks in global supply chains: A review and research agenda. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020;58:44–64. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2019.1629670. - DOI
-
- Vargas–Hernández J.G. Relocation Strategy of Global Supply Chain and Value Chain under Deglobalization. Manag. Inflat. Supply Chain Disrupt. Glob. Econ. 2023;1:62–80.
-
- Almakayeel N., Desai S., Alghamdi S., Qureshi M.R.N.M. Smart Agent System for Cyber Nano–Manufacturing in Industry 4.0. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:6143. doi: 10.3390/app12126143. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources