An Attempt to Develop a Model of Brain Waves Using Quantitative Electroencephalography with Closed Eyes in K1 Kickboxing Athletes-Initial Concept
- PMID: 37112480
- PMCID: PMC10145354
- DOI: 10.3390/s23084136
An Attempt to Develop a Model of Brain Waves Using Quantitative Electroencephalography with Closed Eyes in K1 Kickboxing Athletes-Initial Concept
Abstract
Background: Brain injuries are a common problem in combat sports, especially in disciplines such as kickboxing. Kickboxing is a combat sport that has several variations of competition, with the most contact-oriented fights being carried out under the format of K-1 rules. While these sports require a high level of skill and physical endurance, frequent micro-traumas to the brain can have serious consequences for the health and well-being of athletes. According to studies, combat sports are one of the riskiest sports in terms of brain injuries. Among the sports disciplines with the highest number of brain injuries, boxing, mixed martial arts (MMA), and kickboxing are mentioned.
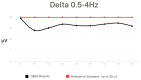
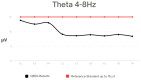
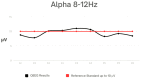
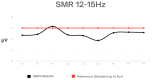
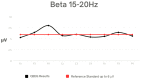
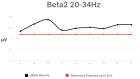
Methods: The study was conducted on a group of 18 K-1 kickboxing athletes who demonstrate a high level of sports performance. The subjects were between the ages 18 and 28. QEEG (quantitative electroencephalogram) is a numeric spectral analysis of the EEG record, where the data is digitally coded and statistically analysed using the Fourier transform algorithm. Each examination of one person lasts about 10 min with closed eyes. The wave amplitude and power for specific frequencies (Delta, Theta, Alpha, Sensorimotor Rhythm (SMR), Beta 1, and Beta2) were analysed using 9 leads.
Results: High values were shown in the Alpha frequency for central leads, SMR in the Frontal 4 (F4 lead), Beta 1 in leads F4 and Parietal 3 (P3), and Beta2 in all leads.
Conclusions: The high activity of brainwaves such as SMR, Beta and Alpha can have a negative effect on the athletic performance of kickboxing athletes by affecting focus, stress, anxiety, and concentration. Therefore, it is important for athletes to monitor their brainwave activity and use appropriate training strategies to achieve optimal results.
Keywords: K-1; QEEG; brain; brain injury; kickboxing; martial arts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preliminary Development of a Brainwave Model for K1 Kickboxers Using Quantitative Electroencephalography (QEEG) with Open Eyes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 17;24(10):8882. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108882. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240227 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding concussion knowledge and behavior among mixed martial arts, boxing, kickboxing, and Muay Thai athletes and coaches.Phys Sportsmed. 2020 Nov;48(4):417-423. doi: 10.1080/00913847.2020.1729668. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Phys Sportsmed. 2020. PMID: 32067547
-
The Effect of Inspiratory Muscle Training on The Pulmonary Function in Mixed Martial Arts and Kickboxing Athletes.J Hum Kinet. 2022 Feb 10;81:53-63. doi: 10.2478/hukin-2022-0005. eCollection 2022 Jan. J Hum Kinet. 2022. PMID: 35291646 Free PMC article.
-
Rating of Perceived Exertion for Quantification of Training and Combat Loads During Combat Sport-Specific Activities: A Short Review.J Strength Cond Res. 2017 Oct;31(10):2889-2902. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002047. J Strength Cond Res. 2017. PMID: 28933715 Review.
-
Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training in Combat Sports: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.J Strength Cond Res. 2020 Mar;34(3):888-900. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000003255. J Strength Cond Res. 2020. PMID: 31904713
Cited by
-
Brain Punch: K-1 Fights Affect Brain Wave Activity in Professional Kickboxers.Sports Med. 2024 Dec;54(12):3169-3179. doi: 10.1007/s40279-024-02082-5. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 39112919 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary Development of a Brainwave Model for K1 Kickboxers Using Quantitative Electroencephalography (QEEG) with Open Eyes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 17;24(10):8882. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108882. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240227 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Electroencephalography (EEG) in Combat Sports-Review of Findings, Perspectives, and Limitations.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 10;14(12):4113. doi: 10.3390/jcm14124113. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40565858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Use of Quantitative Electroencephalography (QEEG) to Assess Post-COVID-19 Concentration Disorders in Professional Pilots: An Initial Concept.Brain Sci. 2023 Aug 30;13(9):1264. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13091264. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37759865 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of physical exercise during competitions and in simulated conditions on hormonal-neurophysiological relationships in kickboxers.Biol Sport. 2024 Jul;41(3):61-68. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2024.133662. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Biol Sport. 2024. PMID: 38952906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Di Marino S. A Complete Guide to Kickboxing. Enslow Publishing; New York, NY, USA: 2018.
-
- Rydzik Ł. Indices of technical and tactical training during kickboxing at different levels of competition in the K1 Formula. J. Kinesiol. Exerc. Sci. 2022;31:1–5. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0015.7542. - DOI
-
- Green G.A., Pollack K.M., D’Angelo J., Schickendantz M.S., Caplinger R., Weber K., Valadka A., McAllister T.W., Dick R.W., Mandelbaum B., et al. Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Major and Minor League Baseball Players. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015;43:1118–1126. doi: 10.1177/0363546514568089. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Georges A., Das J.M. Traumatic Brain Injury. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

