Potentially Toxic Element Contamination in Soils Affected by the Antimony Mine Spill in Northwest China
- PMID: 37112586
- PMCID: PMC10140868
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11040359
Potentially Toxic Element Contamination in Soils Affected by the Antimony Mine Spill in Northwest China
Abstract
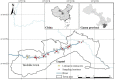
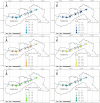
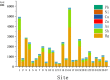
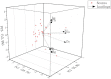
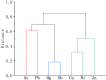
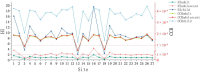
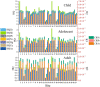
This study provides a comprehensive assessment of the potential ecological and health risks in the area of the antimony mine spill in Longnan, Northwest China, and identifies the sources of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in the soil as a result of the spill. The geo-accumulation index and enrichment factor show that the study area is highly contaminated with arsenic (As), mercury (Hg) and antimony (Sb). The ecological risk index in the tailings spill area ranged from 320.43 to 5820.46 (mean: 1489.82), indicating a very-high potential ecological risk, with mean values of 104.86, 1118.87 and 248.84 for As, Hg and Sb, respectively. The multivariate statistical analysis suggested that Sb and Hg come from tailings leakage, while copper (Cu), nickel (Ni) and zinc (Zn) may be imported from natural sources, and As and lead (Pb) originate from agricultural activities. In addition As and Sb pose a high health risk. With the exception of the non-carcinogenic risk in adults, all other risks are significantly exceeded in other populations, with children being the highest-risk group. These findings provide important quantitative information for the assessment and management of PTE contamination in other tailings spill areas.
Keywords: antimony; mining spill; multivariate analysis; potentially toxic elements; risk assessment; soil pollution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Sources Identification, Ecological Risk Assessment, and Controlling Factors of Potentially Toxic Elements in Typical Lead-Zinc Mine Area, Guizhou Province, Southwest China].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2022 Apr 8;43(4):2081-2093. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202109024. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2022. PMID: 35393832 Chinese.
-
Pollution Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Soils around the Yanzhuang Gold Mine Tailings Pond, Pinggu County, Beijing, China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 6;18(14):7240. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147240. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34299689 Free PMC article.
-
Copper mining in the eastern Amazon: an environmental perspective on potentially toxic elements.Environ Geochem Health. 2022 Jun;44(6):1767-1781. doi: 10.1007/s10653-021-01051-5. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Environ Geochem Health. 2022. PMID: 34676510
-
Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils around China's gold mines: a meta-analysis.Environ Geochem Health. 2022 Nov;44(11):3765-3777. doi: 10.1007/s10653-021-01175-8. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Environ Geochem Health. 2022. PMID: 35037140 Review.
-
Environmental and health risk assessment of potentially toxic trace elements in soils near uranium (U) mines: A global meta-analysis.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Apr 10;816:151556. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151556. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 34752878 Review.
Cited by
-
Occupational, environmental, and toxicological health risks of mining metals for lithium-ion batteries: a narrative review of the Pubmed database.J Occup Med Toxicol. 2024 Aug 27;19(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12995-024-00433-6. J Occup Med Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39192280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Negligible Ecological Risks of Urban Wetlands Caused by Cd and Hg on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China.Toxics. 2023 Jul 28;11(8):654. doi: 10.3390/toxics11080654. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37624160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adebayo A.S., Olufemi A.P., Ogundele L.T., Okunnuwa O.Q., Toyeje A.B., Olowookere C.J. Ecological and human health risk assessments of metals in soil and tailing from Ife-Ijesha gold mining area, Southwest Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022;81:462. doi: 10.1007/s12665-022-10581-9. - DOI
-
- Andreu-Sanchez O., Garcia-Lorenzo M.L., Esbri J.M., Sanchez-Donoso R., Iglesias-Martinez M., Arroyo X., Crespo-Feo E., Ruiz-Costa N., Roca-Perez L., Castineiras P. Soil and Freshwater Bioassays to Assess Ecotoxicological Impact on Soils Affected by Mining Activities in the Iberian Pyrite Belt. Toxics. 2022;10:353. doi: 10.3390/toxics10070353. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fiuza A., Futuro A., Gois J., Dinis M.L., Vila C., Carvalho S., Fernandes A. The Legacy of Potential Environmental Soil Contamination in an Antimony Mining Heritage Area. Minerals. 2023;13:257. doi: 10.3390/min13020257. - DOI
-
- Simic S.B., Miljkovic P., Baumgertel A., Lukic S., Ljubicic J., Cakmak D. Environmental and Health Risk Assessment Due to Potentially Toxic Elements in Soil near Former Antimony Mine in Western Serbia. Land. 2023;12:421. doi: 10.3390/land12020421. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

