Advances in the Utilization of Zebrafish for Assessing and Understanding the Mechanisms of Nano-/Microparticles Toxicity in Water
- PMID: 37112607
- PMCID: PMC10142380
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11040380
Advances in the Utilization of Zebrafish for Assessing and Understanding the Mechanisms of Nano-/Microparticles Toxicity in Water
Abstract
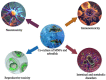
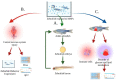
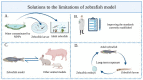
A large amount of nano-/microparticles (MNPs) are released into water, not only causing severe water pollution, but also negatively affecting organisms. Therefore, it is crucial to evaluate MNP toxicity and mechanisms in water. There is a significant degree of similarity between the genes, the central nervous system, the liver, the kidney, and the intestines of zebrafish and the human body. It has been shown that zebrafish are exceptionally suitable for evaluating the toxicity and action mechanisms of MNPs in water on reproduction, the central nervous system, and metabolism. Providing ideas and methods for studying MNP toxicity, this article discusses the toxicity and mechanisms of MNPs from zebrafish.
Keywords: nano-/microparticles; toxicity evaluation; toxicological mechanism; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transgenerational impacts of micro(nano)plastics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment.J Hazard Mater. 2023 Feb 5;443(Pt B):130274. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130274. Epub 2022 Oct 28. J Hazard Mater. 2023. PMID: 36327853 Review.
-
Toxicological impacts of micro(nano)plastics in the benthic environment.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Aug 25;836:155620. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155620. Epub 2022 May 1. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35508242 Review.
-
Key mechanisms of micro- and nanoplastic (MNP) toxicity across taxonomic groups.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021 Sep;247:109056. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.109056. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33894368 Review.
-
Acute ZnO nanoparticles exposure induces developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage in embryo-larval zebrafish.Aquat Toxicol. 2013 Jul 15;136-137:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.03.019. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Aquat Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23643724
-
Folic acid magnetic nanotheranostics for delivering doxorubicin: Toxicological and biocompatibility studies on Zebrafish embryo and larvae.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 1;358:23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.09.009. Epub 2018 Sep 8. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30205093
Cited by
-
Impacts of Environmental Concentrations of Nanoplastics on Zebrafish Neurobehavior and Reproductive Toxicity.Toxics. 2024 Aug 21;12(8):617. doi: 10.3390/toxics12080617. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39195719 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a feasible fast-track testing method for developmental neurotoxicity studies: alternative model for risk assessment of micro- and nanoplastics.Front Toxicol. 2025 Apr 15;7:1567225. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2025.1567225. eCollection 2025. Front Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40303462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zebrafish in dermatology: a comprehensive review of their role in investigating abnormal skin pigmentation mechanisms.Front Physiol. 2023 Nov 23;14:1296046. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1296046. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 38074315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotoxicity of Some Environmental Pollutants to Zebrafish.Life (Basel). 2024 May 17;14(5):640. doi: 10.3390/life14050640. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38792660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioral Studies of Zebrafish Reveal a New Perspective on the Reproductive Toxicity of Micro- and Nanoplastics.Toxics. 2024 Feb 26;12(3):178. doi: 10.3390/toxics12030178. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 38535911 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sarkar B., Dissanayake P.D., Bolan N.S., Dar J.Y., Kumar M., Haque M.N., Mukhopadhyay R., Ramanayaka S., Biswas J.K., Tsang D.C.W., et al. Challenges and opportunities in sustainable management of microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment. Environ. Res. 2022;207:112179. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112179. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

