A Phase 1, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled and Dose-Escalation Study to Evaluate the Safety and Immunogenicity of the Intranasal DelNS1-nCoV-RBD LAIV for COVID-19 in Healthy Adults
- PMID: 37112634
- PMCID: PMC10143096
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11040723
A Phase 1, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled and Dose-Escalation Study to Evaluate the Safety and Immunogenicity of the Intranasal DelNS1-nCoV-RBD LAIV for COVID-19 in Healthy Adults
Abstract
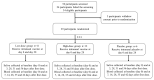
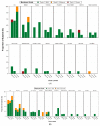
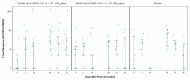
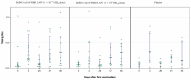
An intranasal COVID-19 vaccine, DelNS1-based RBD vaccines composed of H1N1 subtype (DelNS1-nCoV-RBD LAIV) was developed to evaluate the safety and immunogenicity in healthy adults. We conducted a phase 1 randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study on healthy participants, age 18-55 and COVID-19 vaccines naïve, between March and September 2021. Participants were enrolled and randomly assigned (2:2:1) into the low and high dose DelNS1-nCoV-RBD LAIV manufactured in chicken embryonated eggs or placebo groups. The low and high-dose vaccine were composed of 1 × 107 EID50/ dose and 1 × 107.7 EID50/ dose in 0.2 mL respectively. The placebo vaccine was composed of inert excipients/dose in 0.2 mL. Recruited participants were administered the vaccine intranasally on day 0 and day 28. The primary end-point was the safety of the vaccine. The secondary endpoints included cellular, humoral, and mucosal immune responses post-vaccination at pre-specified time-points. The cellular response was measured by the T-cell ELISpot assay. The humoral response was measured by the serum anti-RBD IgG and live-virus neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV-2. The saliva total Ig antibody responses in mucosal secretion against SARS-CoV-2 RBD was also assessed. Twenty-nine healthy Chinese participants were vaccinated (low-dose: 11; high-dose: 12 and placebo: 6). The median age was 26 years. Twenty participants (69%) were male. No participant was discontinued due to an adverse event or COVID-19 infection during the clinical trial. There was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse events (p = 0.620). For the T-cell response elicited after full vaccination, the positive PBMC in the high-dose group increased to 12.5 SFU/106 PMBC (day 42) from 0 (baseline), while it increased to 5 SFU/106 PBMC (day 42) from 2.5 SFU/106 PBMC (baseline) in the placebo group. The high-dose group showed a slightly higher level of mucosal Ig than the control group after receiving two doses of the vaccine (day 31, 0.24 vs. 0.21, p = 0.046; day 56 0.31 vs. 0.15, p = 0.45). There was no difference in the T-cell and saliva Ig response between the low-dose and placebo groups. The serum anti-RBD IgG and live virus neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV-2 were undetectable in all samples. The high-dose intranasal DelNS1-nCoV-RBD LAIV is safe with moderate mucosal immunogenicity. A phase-2 booster trial with a two-dose regimen of the high-dose intranasal DelNS1-nCoV-RBD LAIV is warranted.
Keywords: COVID-19; DelNS1-nCoV-RBD LAIV; intranasal; phase-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sources had no role in study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation, or writing of the report. The corresponding author had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and immunogenicity of a live-attenuated influenza virus vector-based intranasal SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in adults: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 and 2 trials.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Aug;10(8):749-760. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00131-X. Epub 2022 May 26. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35644168 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 ARCoV mRNA vaccine in Chinese adults: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial.Lancet Microbe. 2022 Mar;3(3):e193-e202. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00280-9. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Lancet Microbe. 2022. PMID: 35098177 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine (ZF2001) in healthy children and adolescents aged 3-17 years in China: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial and an open-label, non-randomised, non-inferiority, phase 2 trial.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2023 Apr;7(4):269-279. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(22)00376-5. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2023. PMID: 36803632 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (inactivated, Vero cell): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Apr 13;22(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05180-1. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33849629 Free PMC article.
-
Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an aerosolised adenovirus type-5 vector-based COVID-19 vaccine (Ad5-nCoV) in adults: preliminary report of an open-label and randomised phase 1 clinical trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2021 Dec;21(12):1654-1664. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00396-0. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34324836 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 intranasal vaccines: current progress, advantages, prospects, and challenges.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(5):2045853. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2045853. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35258416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovation-driven trend shaping COVID-19 vaccine development in China.Front Med. 2023 Dec;17(6):1096-1116. doi: 10.1007/s11684-023-1034-6. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 38102402 Review.
-
Intranasal vaccines for SARS-CoV-2: From challenges to potential in COVID-19 management.Drug Discov Today. 2021 Nov;26(11):2619-2636. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.07.021. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Drug Discov Today. 2021. PMID: 34332100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: A review of newly formed viral clades, pathophysiology, therapeutic strategies and current vaccination tasks.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 15;193(Pt B):1165-1200. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.144. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34710479 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 1 May 2022)]; Available online: https://covid19.who.int.
-
- COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker and Landscape. [(accessed on 1 May 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/coronavirus-dis....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

