Humoral Response in Hemodialysis Patients Post-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccination: A Systematic Review of Literature
- PMID: 37112636
- PMCID: PMC10142871
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11040724
Humoral Response in Hemodialysis Patients Post-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccination: A Systematic Review of Literature
Abstract
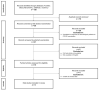
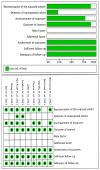
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has infected over 600 million individuals and caused nearly 7 million deaths worldwide (10 January 2023). Patients with renal disease undergoing hemodialysis are among those most adversely affected, with an increased predisposition to SARS-CoV-2 infection and death. This systematic review aimed to pool evidence assessing the humoral response of hemodialysis patients (HDP) post-mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. A systematic search of the literature was performed through MEDLINE, CINAHL, PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science databases, as well as medRxiv and bioRxiv preprint servers up to 10 January 2023. Cohort and case-control studies were included if they reported an immune response in one group of patients undergoing hemodialysis who received mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccination compared with another group of patients receiving the same vaccine but not on hemodialysis. The methodological quality was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Meta-analysis was not deemed appropriate due to the high heterogeneity between studies. From the 120 studies identified, nine (n = 1969 participants) met the inclusion criteria. Most studies (n = 8/9, 88%) were of high or medium methodological quality (≥6/9 stars). The results revealed that HDP developed lower antibody levels across all timepoints post-vaccination when compared with controls. Patients with chronic kidney disease elicited the highest antibody immune response, followed by HDP and, lastly, kidney transplant recipients. Overall, post-vaccination antibody titers were comparatively lower than in the healthy population. Current results imply that robust vaccination strategies are needed to address waning immune responses in vulnerable populations.
Keywords: COVID-19; adaptive immunity; antibody titer; hemodialysis; mRNA-vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. [(accessed on 10 January 2023)]. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/
-
- Diaz R.T., Herrera E.L. COVID-19 in chronic kidney patients: A warning. Rev. Méd. Chile. 2020;148:707–714. - PubMed
-
- Notarte K.I., Ver A.T., Velasco J.V., Pastrana A., Catahay J.A., Salvagno G.L., Yap E.P.H., Martinez-Sobrido L., Torrelles J.B., Lippi G., et al. Effects of age, sex, serostatus, and underlying comorbidities on humoral response post-SARS-CoV-2 Pfizer-BioNTech MRNA vaccination: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2022;59:373–390. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2022.2038539. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous