Impact of COVID-19 Vaccination on Short-Term Perceived Change in Physical Performance among Elite Athletes: An International Survey
- PMID: 37112708
- PMCID: PMC10144569
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11040796
Impact of COVID-19 Vaccination on Short-Term Perceived Change in Physical Performance among Elite Athletes: An International Survey
Abstract
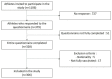
COVID-19 vaccination raised concerns about its potential effects on physical performance. To assess the impact of COVID-19 vaccination on the perceived change in physical performance, we conducted an online survey among elite athletes from Belgium, Canada, France and Luxembourg, with questions about socio-demographics, COVID-19 vaccination, perceived impact on physical performance and perceived pressure to get vaccinated. Full vaccination was defined as two doses of mRNA or vector vaccine or a heterologous vaccine scheme. Among 1106 eligible athletes contacted, 306 athletes answered the survey and were included in this study. Of these, 72% perceived no change in their physical performance, 4% an improvement and 24% a negative impact following full COVID-19 vaccination. For 82% of the included athletes, the duration of the negative vaccine reactions was ≤3 days. After adjustment for potential confounding variables, practicing an individual sport, a duration of vaccine reactions longer than 3 days, a high level of vaccine reaction and the perceived pressure to get vaccinated were independently associated with a perceived negative impact on physical performance of more than 3 days after the vaccination. The perceived pressure to get vaccinated appears to be a parameter associated with the negative perceived change in the physical performance and deserves further consideration.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; athletes; athletic performance; elite; immunization; sports.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any potential conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sports Elite Means Vaccine Elite? Concerns and Beliefs Related to COVID-19 Vaccines among Olympians and Elite Athletes.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 8;10(10):1676. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10101676. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36298541 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine versus infection - COVID-19-related loss of training time in elite athletes.J Sci Med Sport. 2022 Dec;25(12):950-959. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2022.10.004. Epub 2022 Oct 12. J Sci Med Sport. 2022. PMID: 36253224 Free PMC article.
-
Period prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infections and willingness to vaccinate in Swiss elite athletes.BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2022 Jun 29;8(2):e001330. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2022-001330. eCollection 2022. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2022. PMID: 35789552 Free PMC article.
-
A Guide to Different Intensities of Exercise, Vaccination, and Sports Nutrition in the Course of Preparing Elite Athletes for the Management of Upper Respiratory Infections during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Narrative Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 8;19(3):1888. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19031888. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35162910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Trunk Muscle Training on Physical Fitness and Sport-Specific Performance in Young and Adult Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2022 Jul;52(7):1599-1622. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01637-0. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 35061213 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mpox in sports: A comprehensive framework for anticipatory planning and risk mitigation in football based on lessons from COVID-19.Biol Sport. 2024 Oct;41(4):317-335. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2024.144014. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Biol Sport. 2024. PMID: 39416489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Impact of COVID-19 on Physical Activity One Month after Infection and Its Potential Determinants: Re-Infections, Pre-Illness Vaccination Profiles/Types, and Beyond.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;11(9):1431. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11091431. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37766108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martens G., Delvaux F., Forthomme B., Kaux J.F., Urhausen A., Bieuzen F., Leclerc S., Winkler L., Brocherie F., Nedelec M., et al. Exercise-Based Injury Prevention in High-Level and Professional Athletes: Narrative Review and Proposed Standard Operating Procedure for Future Lockdown-Like Contexts after COVID-19. Front. Sport Act. Living. 2021;3:745765. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2021.745765. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dighriri I.M., Alhusayni K.M., Mobarki A.Y., Aljerary I.S., Alqurashi K.A., Aljuaid F.A., Alamri K.A., Mutwalli A.A., Maashi N.A., Aljohani A.M., et al. Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine (BNT162b2) Side Effects: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2022;14:e23526. doi: 10.7759/cureus.23526. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meyer T., Wolfarth B., Gärtner B. Recommendations for Athletes to Vaccinate against SARS-CoV-2. Dtsch. Z. Sportmed./Ger. J. Sport Med. 2021;72:E1–E4. doi: 10.5960/dzsm.2021.486. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous