Immunogenicity and Protection against Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus in Swine Intradermally Vaccinated with a Bivalent Vaccine of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Type O and A
- PMID: 37112726
- PMCID: PMC10142530
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11040815
Immunogenicity and Protection against Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus in Swine Intradermally Vaccinated with a Bivalent Vaccine of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Type O and A
Abstract
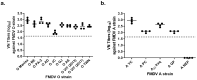
Following the worst outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD), a highly contagious disease in cloven-hoofed animals caused by the FMD virus, from November 2010-April 2011, the Korean government enforced a mandatory vaccination policy. A bivalent (FMD type O and A; O + A) vaccine has been recently implemented. Although the FMD outbreak was suppressed by vaccination, the intramuscular (IM) injection presents side effects. Therefore, improving FMD vaccine quality is necessary. Here, we investigated the side effects and immune efficacy of the O + A bivalent vaccine using two different routes of administration: intradermal (ID) and IM. To compare the immune efficacy of the two inoculation routes, virus neutralization titers and structural protein (antigen) levels were measured. The protective efficacy of ID vaccines was confirmed using two viruses (FMDV O/AS/SKR/2019 and A/GP/SKR/2018) isolated in the Republic of Korea. Serological analysis revealed that both animals administered by ID and IM injections exhibited equal immune efficacy. A virus challenge test in the target animal (swine) revealed no (or extremely low) clinical symptoms. Swine in the ID injected group exhibited no side effects. In conclusion, we suggest that the ID route of vaccination is an effective alternative to the existing IM route, which is associated with more frequent side effects.
Keywords: foot-and-mouth disease; intradermal vaccination; type A; type O.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhanced Effects of ISA 207 Adjuvant via Intradermal Route in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine for Pigs.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Aug 26;12(9):963. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12090963. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339996 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-protective efficacy of the O1 Manisa + O 3039 bivalent vaccine and the O 3039 monovalent vaccine against heterologous challenge with FMDV O/Jincheon/SKR/2014 in pig.Vaccine. 2019 Mar 14;37(12):1702-1709. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.11.080. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 30712811
-
Intradermal Inoculation of Inactivated Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine Induced Effective Immune Responses Comparable to Conventional Intramuscular Injection in Pigs.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Feb 13;12(2):190. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12020190. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38400173 Free PMC article.
-
Intradermal vaccination of pigs against FMD with 1/10 dose results in comparable vaccine efficacy as intramuscular vaccination with a full dose.Vaccine. 2009 Feb 18;27(8):1272-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.12.011. Epub 2008 Dec 27. Vaccine. 2009. PMID: 19114077
-
Targeted FMD Vaccines for Eastern Africa: The AgResults Foot and Mouth Disease Vaccine Challenge Project.Viruses. 2021 Sep 14;13(9):1830. doi: 10.3390/v13091830. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34578411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a Vaccine Candidate Designed for Broad-Spectrum Protection against Type A Foot-and-Mouth Disease in Asia.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jan 9;12(1):64. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12010064. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38250877 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Effects of ISA 207 Adjuvant via Intradermal Route in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine for Pigs.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Aug 26;12(9):963. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12090963. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339996 Free PMC article.
-
Duration of the antibody response following intradermal administration of a quarter-dose oil adjuvant foot-and-mouth disease vaccine in sheep.Vet Res Commun. 2025 Feb 26;49(2):119. doi: 10.1007/s11259-025-10686-z. Vet Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40009272
-
Simple and High-Throughput Quantification of Mono- and Bivalent Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Vaccine Antigens by Differential Scanning Fluorimetry.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Jul 2;13(7):721. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13070721. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40733699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park J.H., Lee K.N., Ko Y.J., Kim S.M., Lee H.S., Park J.Y., Yeh J.Y., Kim M.J., Lee Y.H., Sohn J.J., et al. Diagnosis and control measures of the 2010 outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease A type in the Republic of Korea. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013;60:188–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1865-1682.2012.01333.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

